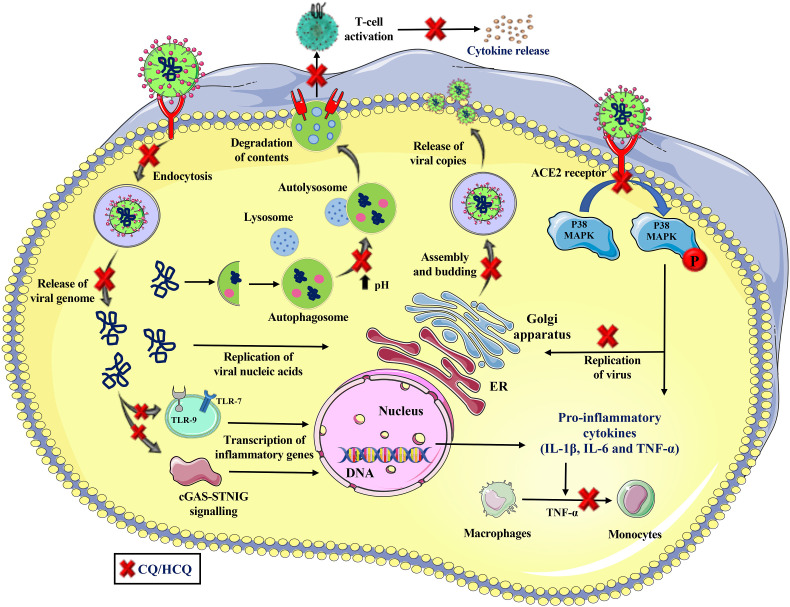
Fig. 2.
A Multitude of mechanisms by which CQ/HCQ may work in COVID-19. CQ/HCQ may prevent the entry of virus (either by blocking endocytosis or inhibition of the N-glycosylation of the cell surface viral receptor ACE2 or the viral spike (S) proteins or inhibition of the synthesis of cell membrane sialic acids) and release of viral genome leading to reduction in transcription of inflammatory genes and induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines. CQ/HCQ can also modulate innate and adaptive immune cell activation, cytokine response and inflammation by various mechanisms that leads to reduction in cellular inflammation. CQ/HCQ also affects viral replication, assembly and budding of viral proteins leading to reduction in viral copies in the host cells.