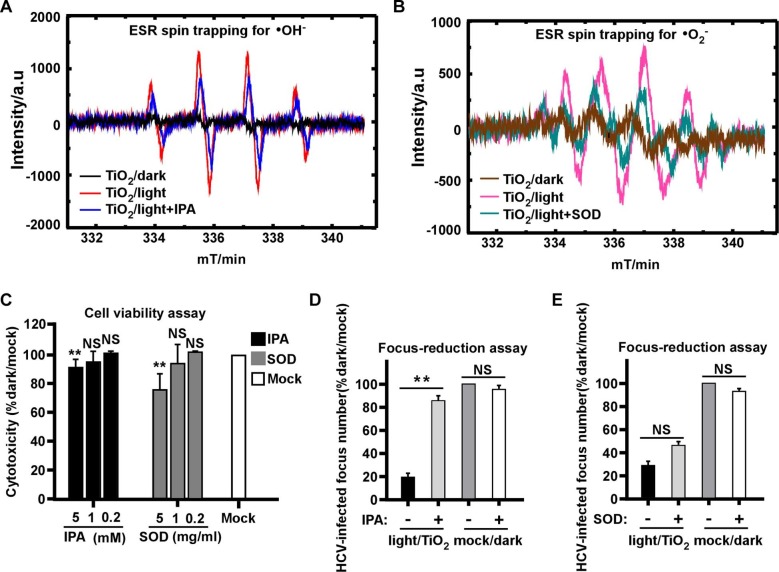
Fig. 5.
The hydroxyl radicals mediate antiviral effect of illuminated TiO2. The radiation intensity was 0.4 mW/cm2 at wavelength of 375 nm for the “light” condition. (A) Hydroxyl radicals (•OH) were detected by DMPO spin trap of TiO2 illuminated for 10 min in the presence or absence of 1 mM isopropanol (IPA) as the quenching agent, or kept in dark. (B) Superoxide radicals (•O2−) were detected by DMPO spin trap of TiO2 illuminated for 10 min in the presence or absence of 1 mg/ml Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) as the quenching agent, or kept in dark. (C) Cytotoxicity of different dose of IPA or SOD that respectively quenches •OH and •O2− radicals in Huh7.5.1 cells for 2 days was evaluated using cell titer assay. (D-E) The effect of 60 min illuminated TiO2 on HCV in the presence of IPA (D) or SOD (E) was determined by the focus-reduction assay. Viral infectivity titers were expressed as a percentage of the value to the mock/dark group. The error bars in panel C were derived from triplicates. **, P<0.01; *, P<0.05; NS, P>0.05.