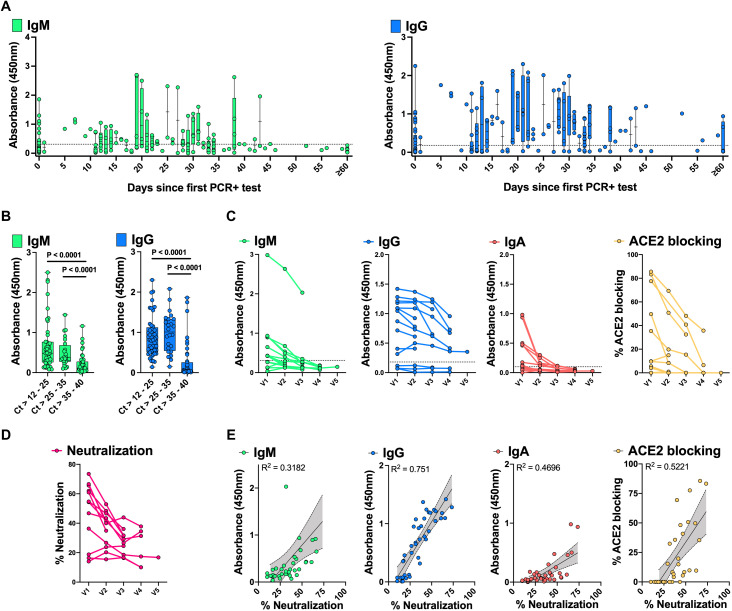
Fig. 4. Development of anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD antibody responses in SARS-CoV-2 rRT-PCR+ asymptomatic individuals and outpatients over time.
176 plasma samples from 136 SARS-CoV-2 rRT-PCR+ individuals were tested for RBD IgM and IgG. The x-axis indicates the time following the first positive rRT-PCR test (A). Dotted lines denote the assay cutoff for positive results. RBD IgM and IgG are shown for the latest available timepoint for subjects with low (Ct >12-25), middle (Ct >25-35) and high (Ct >35-40) SARS-CoV-2 rRT-PCR Ct at diagnosis (B). 45 plasma samples collected from 14 rRT-PCR+ asymptomatic individuals and outpatients sampled at monthly intervals (V1 = enrollment, V2 to V5 = months 1 to 4 post-enrollment) were tested for RBD IgM, IgG, IgA at a dilution of 1:100, as well as RBD-ACE2 blocking antibodies at a dilution of 1:10 (C). The 45 plasma samples were further tested for pseudoviral neutralization at a dilution of 1:1250 (D). Box-whisker ELISA OD450 and blocking/neutralization percent plots show the interquartile range as the box and the minimum and maximum values as the ends of the whiskers. Correlations between virus neutralization and RBD IgM, IgG, IgA, and RBD-ACE2 blocking are shown with superimposed simple linear regression and 95% confidence bands (grey shading) of the best-fit line (E). Plots show mean ELISA OD450 values of duplicate measurements and average percent neutralization from duplicate testing in each of two replicate experiments.