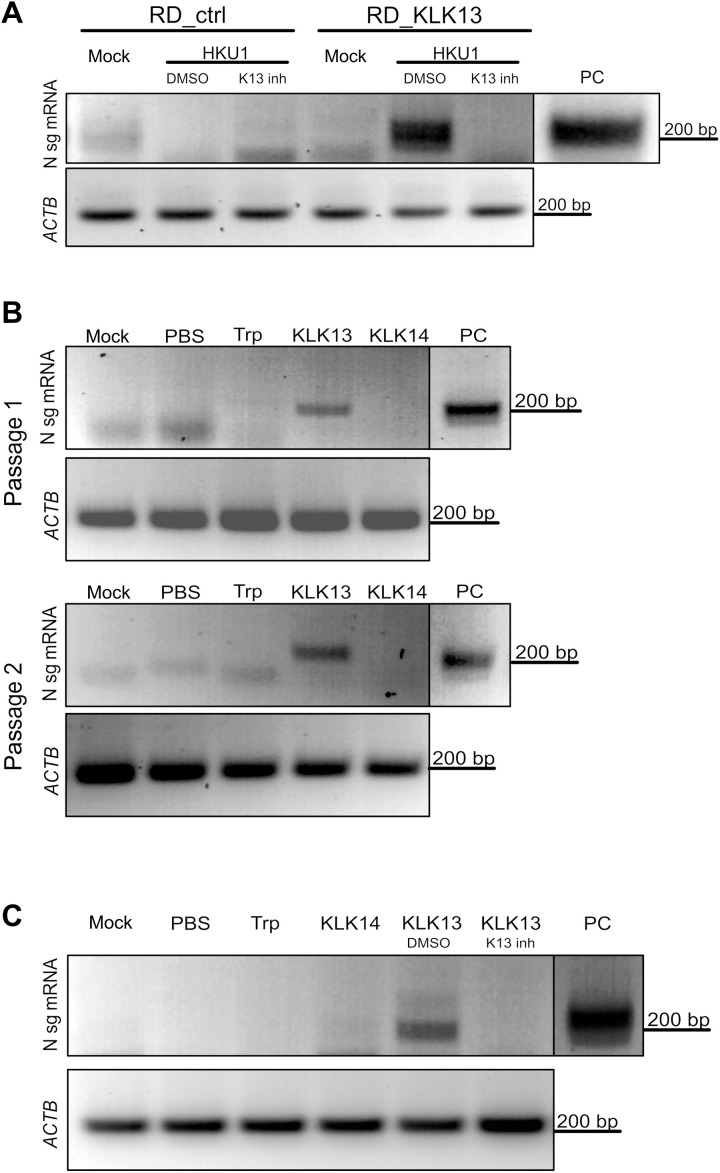
Fig. 5. HCoV-HKU1 replicates in RD cells expressing KLK13.
(A) Control (RD_ctrl) and KLK13-expressing RD cells (RD_KLK13) were inoculated with HCoV-HKU1 (106 RNA copies/ml) or were left uninfected (mock) in the presence of 10 μM KLK 13 inhibitor (K13 inh) or with DMSO as a control. After 7 days of culture at 32°C, total RNA was isolated and reverse-transcribed, and subgenomic mRNA for the viral N protein was detected by seminested PCR analysis. ACTB was used as an internal control. PC, positive control from virus-infected HAE cultures. (B) HCoV-HKU1 was incubated with 200 nM trypsin (Trp), KLK13, KLK14, or PBS for 2 hours at 32°C and further applied onto the RD cells. Top: After 7 days at 32°C, total RNA was isolated and reverse-transcribed, and subgenomic mRNA for the viral N protein was detected by seminested PCR analysis (passage 1). Bottom: In addition, 1 ml of the cell culture medium was harvested and applied to freshly seeded RD cells with medium supplemented with fresh enzymes. After 7 days at 32°C, subgenomic mRNA for the N protein was detected by seminested PCR (passage 2). ACTB was used as an internal control. (C) HCoV-HKU1 was incubated with 200 nM trypsin (Trp), KLK14, KLK13, KLK13 in the presence of the KLK13 inhibitor (K13 inh), DMSO (DMSO), or PBS for 2 hours at 32°C and further applied onto RD cells. Subgenomic mRNA for N protein was detected by seminested PCR. ACTB was used as an internal control. The vertical black lines indicate that the lanes are not contiguous.