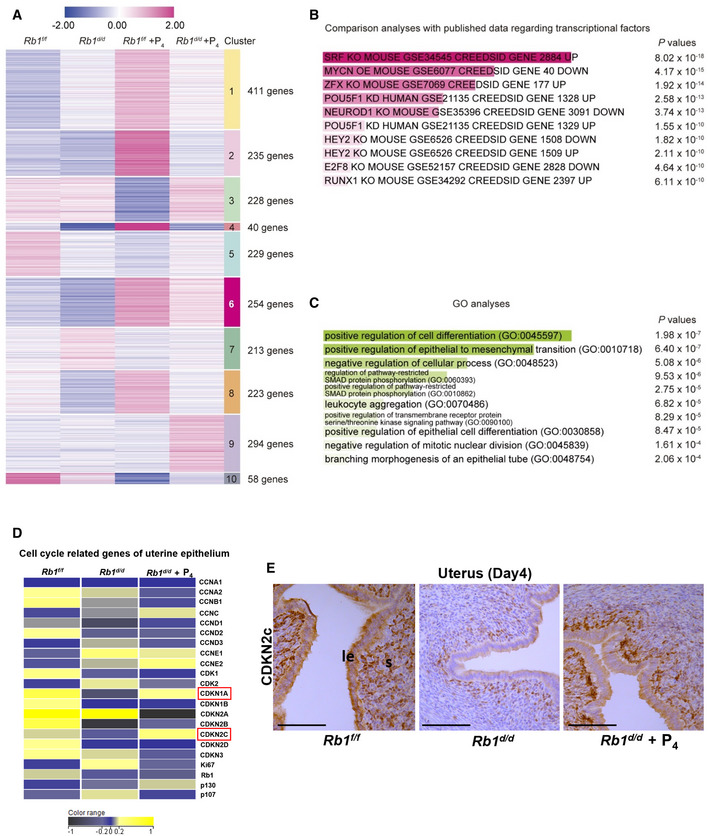
Day 4 uteri were collected from Rb1f/f, Rb1d/d, P4‐primed Rb1f/f, and P4‐primed Rb1d/d mice. As for P4‐primed Rb1f/f and Rb1d/d mice, pre‐implantation P4 treatment (2 mg/mouse/day) was performed on days 2 and 3 of pregnancy. RNA‐seq was performed using the uterine luminal epithelium dissected out by laser capture microdissection. The heatmaps depicted log2 fold enrichment of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) among the uterine epithelium. Clusters were defined by k‐means clustering. Each DEG has a log2 fold change > |1| in at least one group comparing to others. Numbers shown in right indicate different gene clusters and numbers of DEGs in each cluster.
Gene regulatory systems in the gene cluster 6 in which the transcripts are poorly expressed in Rb1d/d mice without P4 supplementation compared with other groups were predicted in Enrichr by comparing our data with publicly available datasets as for transcriptional factors. DEGs in the cluster 6 were highly correlated with cell cycle‐related TFs such as serum response factor (SRF) and E2F8.
GO terms analyses by Enrichr for the cluster 6 demonstrated that the genes related to epithelial differentiation and inhibition of cell proliferation are downregulated in the luminal epithelium of Rb1d/d mice without P4 treatment.
The heatmap of cell cycle‐related genes in the luminal epithelium of Rb1f/f and Rb1d/d mice with and without pre‐implantation P4 treatment was demonstrated. Cyclin‐dependent kinase inhibitors CDKN2A (p21) and CDKN2C (p18) were upregulated in Rb1f/f and Rb1d/d mice with P4 treatment compared with Rb1d/d mice without P4 treatment. Yellow, blue, and black indicate high, intermediate, and low gene expression, respectively.
Immunohistochemistry of CDKN2C (p18) protein in the uterus of Rb1f/f and Rb1d/d mice with and without P4 treatment. Same as transcriptome analysis, CDKN2C staining was intense in the uteri of Rb1f/f and Rb1d/d mice with P4 treatment compared with Rb1d/d mice without P4 treatment. Scale bar = 100 μm; le, luminal epithelium; s, stroma.