Figure 5.
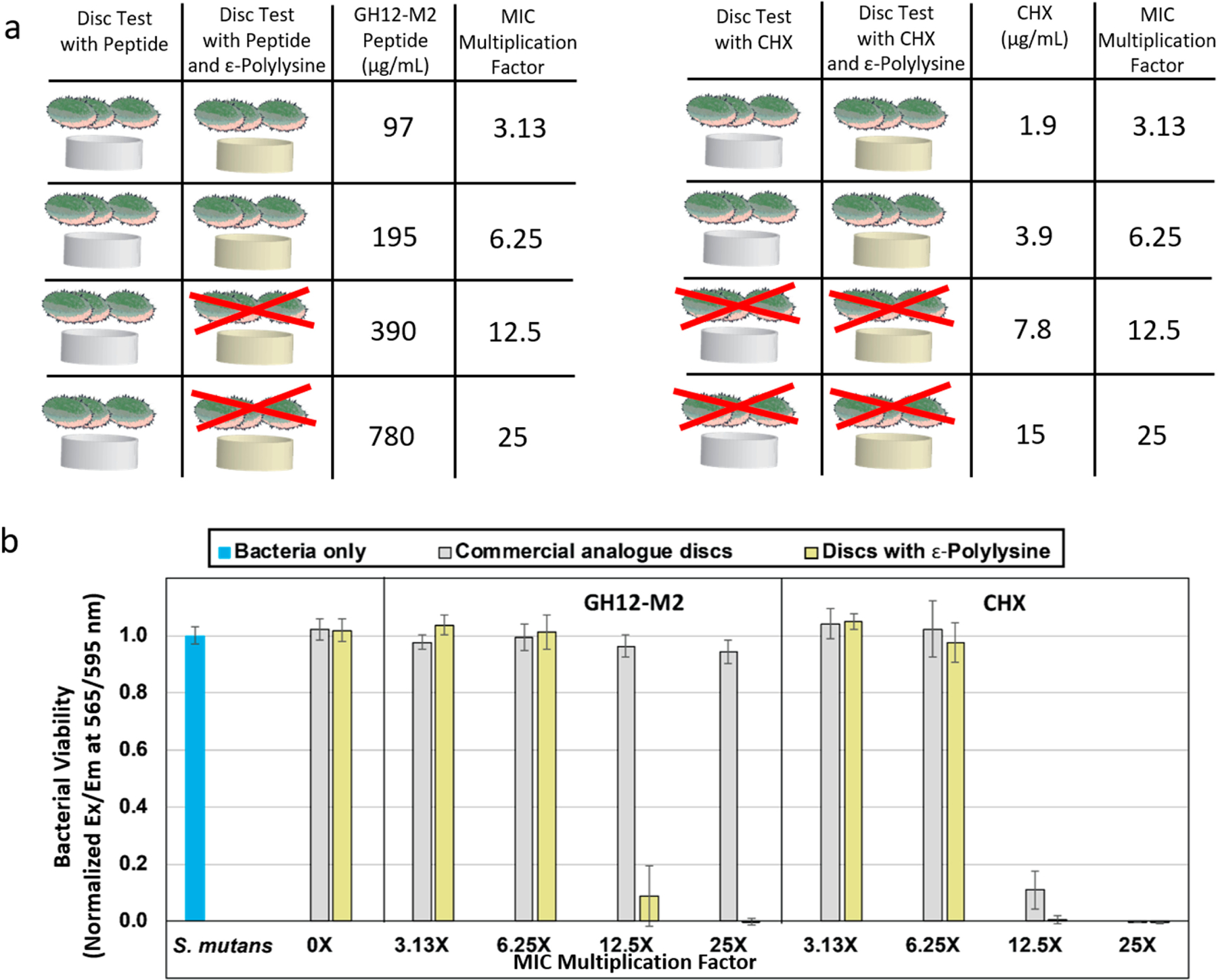
(a) Schematic of adhesive system samples starting with commercial analogue. Experiments included the addition of GH12-M2 antimicrobial peptide onto the discs with ε-polylysine to see bacterial inhibition. As a positive control for antimicrobial activity, chlorhexidine gluconate was added at a multiple of its measured MIC value. 12.5× or greater concentration of CHX was sufficient for bacterial inhibition with or without ε-polylysine. (b) S. mutans UA159 growth/viability based on AlamarBlue assay on dental adhesive discs soaked with either an antimicrobial peptide or a chlorhexidine aqueous solution as a multiple of minimum inhibitory concentration.
