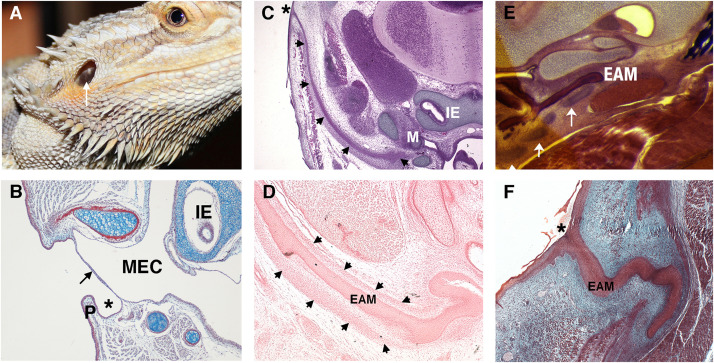
FIGURE 2.
Variations in the non-mammalian ear canal. (A) Bearded dragon (Pogona vitticeps) with superficial tympanic membrane outlined by arrow. (B–F) Histology sections. (B) Sagittal trichrome section of gecko ear showing a shallow ear canal (star) and superficial tympanic membrane (arrow). (C,D) Developing platypus (Ornithorhynchus anatinus) EAM (C) Frontal section of platypus ear at 2 days post hatching (2 p.h.). The developing ear canal (arrows) is long extending from extending form the top of the head to the malleus. There is no pinna at the canal opening (marked by *). (D) Frontal section of developing ear canal in 10 p.h. day platypus. The EAM develops in a sheath of condensed mesenchyme (arrows). (E,F) Developing echidna (Tachyglossus aculeatus) EAM (E) Horizontal section through the EAM of 55–65 p.h. (arrows) days echidna demonstrating cartilage support (arrows) around the developing EAM. (F) Horizontal trichrome section through EAM of an echidna at 18 p.h. days showing a tortuous path to the opening (star). P, Pinna; MEC, middle ear cavity; IE, inner ear; EAM, external auditory meatus.