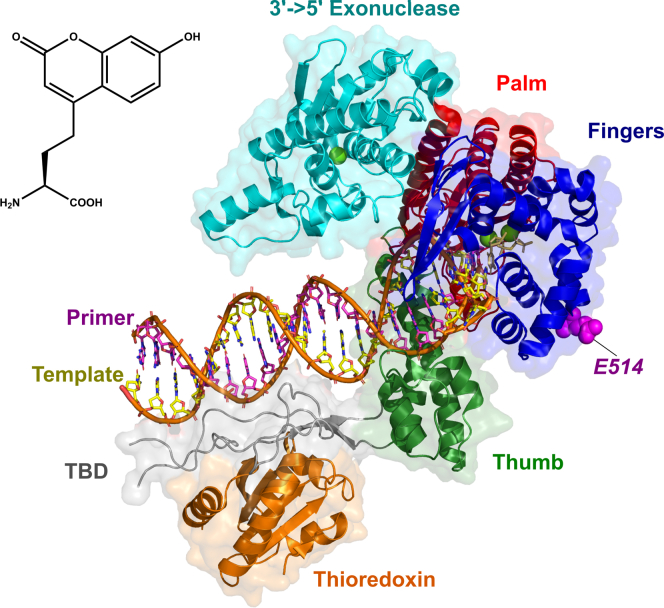
Figure 1.
Structure of fluorescent unnatural amino acid and T7 DNA polymerase.Top left, structure of the fluorescent unnatural amino acid, L-(7-hydroxycoumarin-4-yl) ethylglycine (7-HCou). Right, structure of T7 DNA polymerase: The overall structure resembles a right hand with the polymerase active site situated at the interface of the palm domain (red), fingers domain (blue), and thumb domain (green). 7-HCou is inserted at position 514, on the back side of the fingers domain and is shown as magenta spheres. Thioredoxin (orange) is a 12-kDa host redox protein that associates with T7 gene product 5 through a unique extension of the thumb domain called the thioredoxin binding domain (TBD, gray) and helps with stable primer (magenta)/template (yellow) DNA binding. The 3’-5’ proofreading exonuclease domain (cyan) increases the fidelity of the enzyme by at least a factor of 1000. Magnesium ions are shown as green spheres in the exonuclease and polymerase active sites. The structure was drawn using Pymol from PDBID: 6p7e (41).