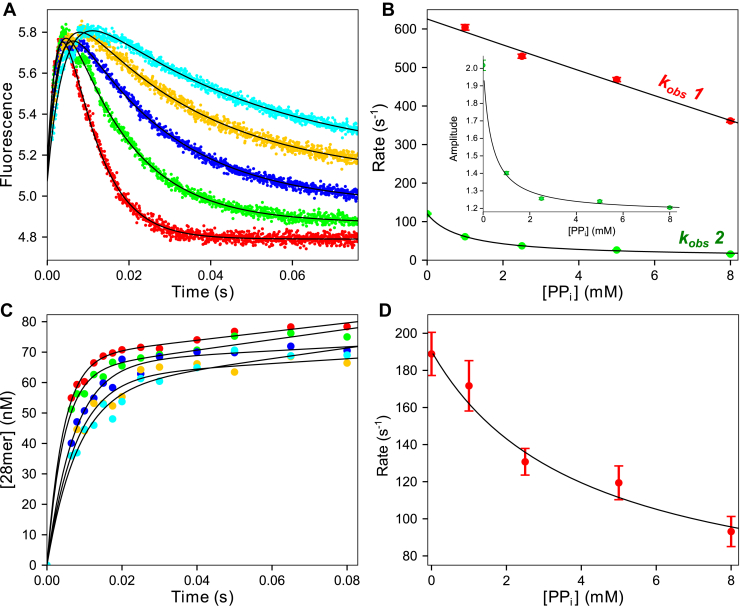
Figure 6.
Kinetics of PPiinhibition on dATP incorporation.A, fluorescence measurement during PPi inhibition on dATP incorporation. T7 DNA polymerase E514Cou (500 nM), thioredoxin (10 μM), 27/45 DNA (600 nM), and PPi (0–8 mM) were mixed with dATP (50 μM) and Mg2+ (12.5 mM) to start the reaction. Data at each concentration were fit to a double exponential function (black lines). B, rate versus PPi concentration for inhibition of dATP incorporation. Rates are from data in (A). Data are shown for the fast phase (red, kobs 1) and slow phase (green, kobs 2), fit to a line and a hyperbola, respectively (black lines). The slope of the linear fit of the slow phase derived from the fitting is −0.028 ± 0.003 mM−1 s−1, which suggests weak competitive inhibition by PPi for binding to the enzyme. The hyperbolic fit to the slow phase gives an apparent Kd,PPi: 775 ± 75 μM. Inset: Amplitude versus PPi concentration for the slow phase, estimating an apparent Kd of 350 ± 80 μM. C, quench flow measurement of PPi inhibition of dATP incorporation. T7 DNA polymerase E514Cou (120 nM), thioredoxin (2.4 μM), FAM-27/45 DNA (200 nM), BSA (0.1 mg/ml), and PPi (0–12 mM) from one syringe were mixed with dATP (20 μM) and Mg2+ (12.5 mM) from the other syringe to start the reaction. Data at each PPi concentration are shown fit to a burst equation (black lines). D, rate versus PPi for inhibition on dATP incorporation. Rates are from data in (C). Data for the exponential phase of the burst at each concentration are shown fit to a hyperbola (black line) and gives an apparent Ki,PPi: 5.9 ± 3.1 mM.