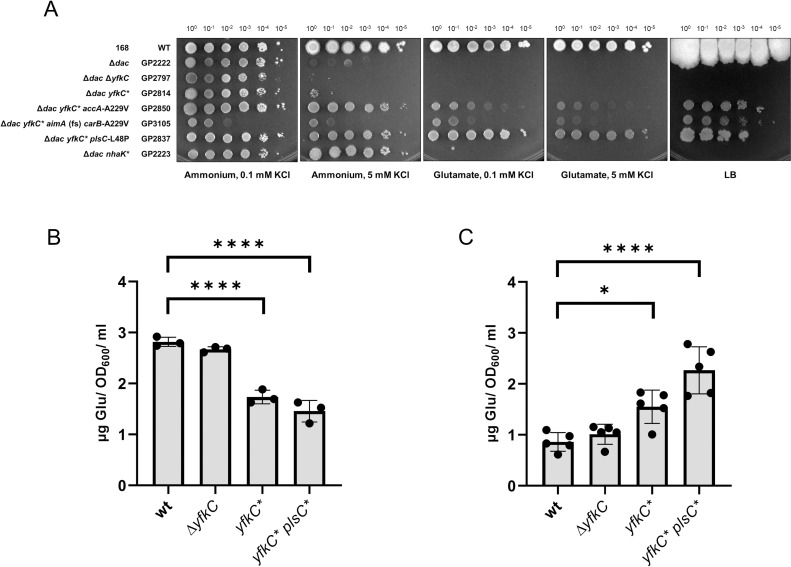
Fig 4. The influence of the mechanosensitive channel YfkC on growth of a B. subtilis strain lacking c-di-AMP in the presence of glutamate.
(A) B. subtilis strains were cultivated in MSSM minimal medium with 0.1 mM KCl and glutamate. Cells were harvested, washed, and the OD600 was adjusted to 1.0. Serial dilutions were dropped onto MSSM minimal plates with the indicated potassium concentration and ammonium or glutamate, or on LB plates. (B) The R42W amino acid substitution in the mechanosensitive channel YfkC reduces intracellular glutamate levels. The intracellular metabolites of B. subtilis wild type strain 168, and the isogenic ΔyfkC, yfkC*, and yfkC* plsC* mutants were extracted and analyzed by GC-MS. (C) The R42W in the mechanosensitive channel YfkC results in an enhanced export of glutamate. The glutamate concentration in the supernatant of B. subtilis cultures of wild type strain 168, and the isogenic ΔyfkC, yfkC*, and yfkC* plsC* mutants were analyzed by GC-MS. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (**** P < 0.0001). The numerical data are presented in S4 Table.