Fig 3.
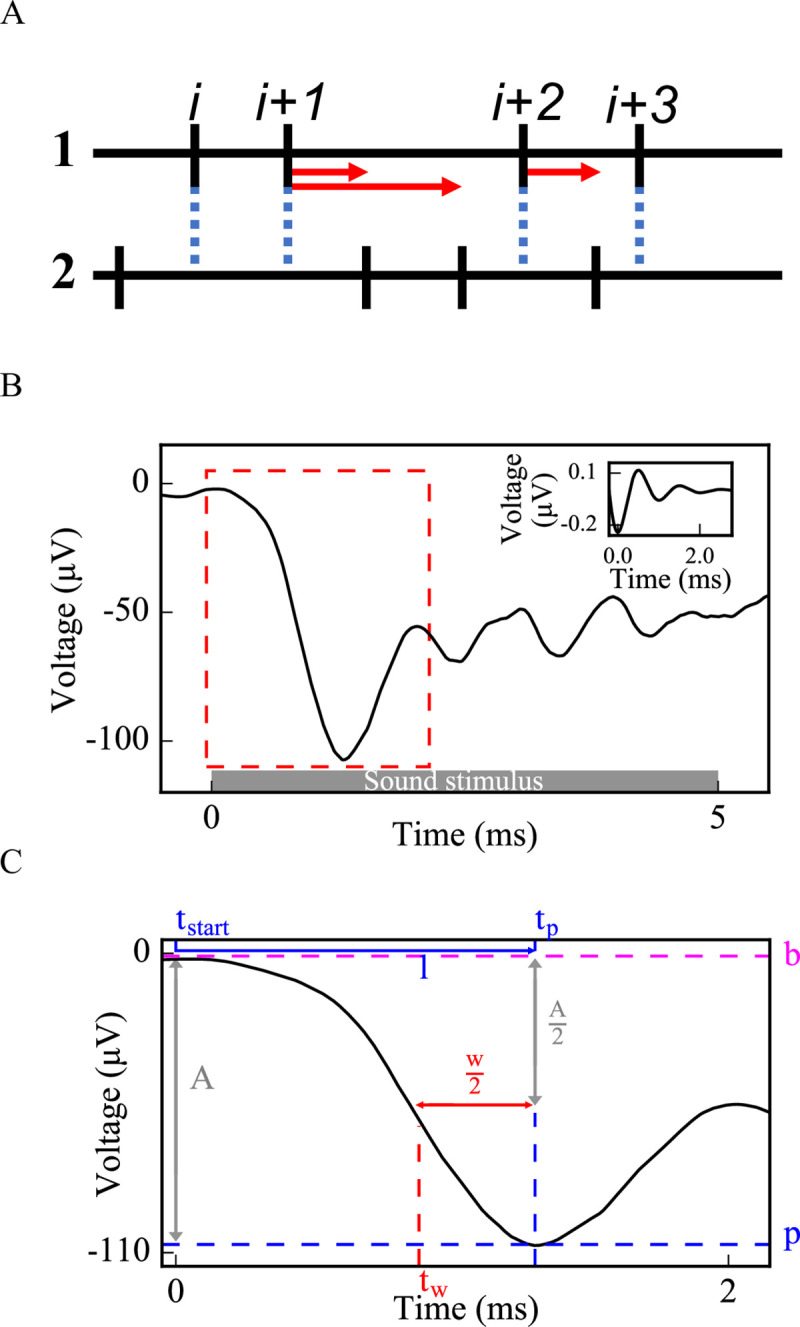
Methods used to evaluate cumulative activity of SGN fiber populations: pairwise spike time differences (A) and simulated CAP (B,C). (A) For each non-identical pair of spike trains (1 and 2) from an SGN fiber population, forward time intervals were measured between each spike i of spike train 1 and all spikes of spike train 2 falling between times of spikes i and i+1. Standard deviations of the distributions of these time intervals were calculated to evaluate synchronous spike timing in the SGN fiber population. (B) Each spike in Fig 2D was convolved with the unitary response of a CAP [the inset of (B)] and convolutions from each spike were summed up to obtain a simulated CAP of the SGN fiber population. (C) Amplitude, latency and width were measured from the first peak of the simulated CAP [dashed rectangle in (B) is zoomed in for (C)] (b: baseline, p: peak, A: amplitude of the peak, tp: peak time, l: latency, w: width, tw: half amplitude time before tp).
