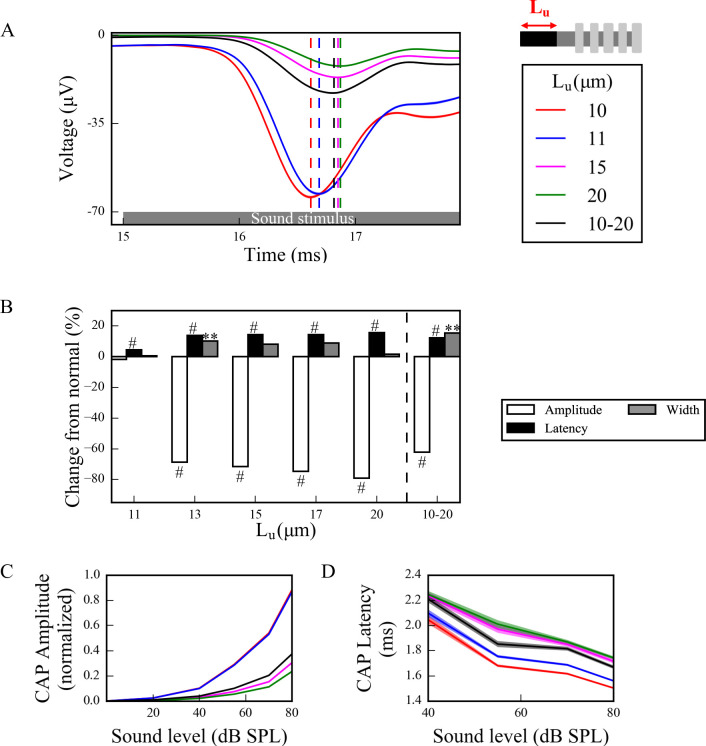
Fig 5. Longer Lu significantly decreases and delays the peak of the sound-evoked CAPs of SGN fibers.
(A) Sound-evoked CAPs of SGN fiber populations with varying unmyelinated segment length Lu at 70dB SPL, averaged over 50 simulations. Shaded regions correspond to the standard error of the mean and dashed lines correspond to the peaks of each CAP, labeled with the same colors as the CAPs. The decrease and delay of peak CAPs were significant for populations with Lu > 11 μm. (B) Comparison of CAP measures of each population relative to normal Lu (Lu = 10 μm) at 70 dB SPL. Latencies were significantly higher for populations with Lu>10 μm and peaks were significantly lower for populations with Lu>11 μm. The increases in widths were only minimal, however significant for the heterogeneous population, where 10 μm ≤ Lu ≤ 20 μm (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, #p<0.001). (C) Normalized CAP amplitudes for various sound levels exhibited an exponential increase and the decreases in CAP amplitudes for populations with Lu>11 μm were more pronounced for higher sound levels. (D) The latencies of CAP peaks increased with higher Lu for all sound levels and decreased along the sound levels.