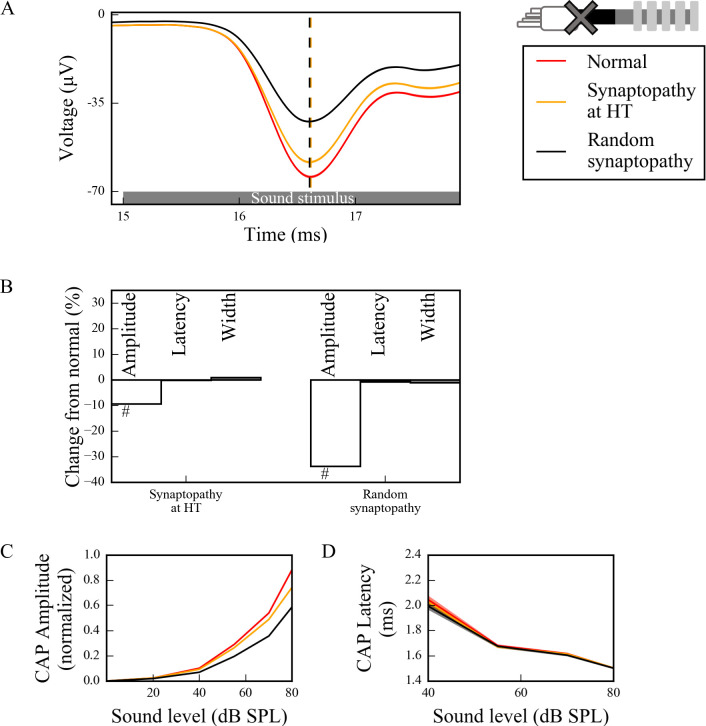
Fig 7. Synaptopathy at IHC-SGN synapses decreases the peak of the CAP significantly, without changes to peak latency and width.
(A) Sound-evoked CAPs of SGN fiber populations with different synaptopathy scenarios at 70dB SPL, averaged over 50 simulations. Shaded regions correspond to the standard error of the mean and dashed lines correspond to the peaks of each CAP, labeled with the same colors as the CAPs. Synaptopathy had smaller effects on CAP peak amplitude and latency when it affected only HT fiber synapses compared to affecting all fiber types randomly. (B) Comparison of CAP measures of synaptopathy cases relative to normal (no synaptopathy) at 70 dB SPL (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, #p<0.001). (C) Normalized CAP amplitudes exhibited an exponential increase and the decreases in CAP amplitudes of populations with both synaptopathy scenarios were more pronounced for higher sound levels. The latencies of the CAP peaks did not exhibit any significant difference between different populations for all sound levels.