Fig. 4. Real-time noninvasive quantification of BSH activity in vivo using the BAL assay.
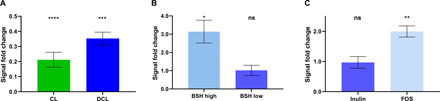
(A) The ratio of bioluminescent signal resulting from FVB + luc mice treated with the antibiotic cocktail (AVNM) for 7 days over untreated animals. The animals received oral gavage of CL (green bar) or DCL (blue bar) probes before and after AVNM treatment (n = 5 per group). (B) The ratio of bioluminescent signal resulting from FVB + luc mice that received oral gavage of DCL probe before and after administration L. plantarum WT (BSH-high) or L. plantarum Δbsh1–4 (BSH-low) bacteria (n = 5 per group). (C) The ratio of bioluminescent signal resulting from the DCL probe administered to FVB + luc mice treated with prebiotics added in drinking water (Inulin or FOS mixture) for 20 days over untreated animals (n = 5 per group). Bar graphs represent the mean ratio of signals after and before the corresponding treatment for each animal with error bars representing ± SEM. Statistical significance (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001) calculated using a one-sample t test with a theoretical mean of 1.
