Fig. 6. DTD2’s ND activity and chiral selectivity are conserved throughout Archaea.
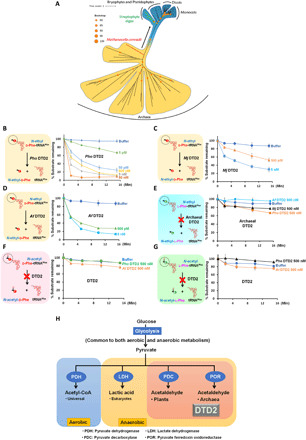
(A) Phylogenetic classification of archaeal and plant DTD2s (generated with scoring matrix LG+R5 (according to the BIC score, of 546 protein models, LG+R5 was chosen as the best amino acid substitution model for the given multiple sequence alignment, which was used to construct a phylogenetic tree). (B) Deacylation of N-ethyl-d-Phe-tRNAPhe (Pho) with Pho DTD2. (C) Deacylation of N-ethyl-d-Phe-tRNAPhe (Pho) with Mj DTD2. (D) Deacylation of N-ethyl-d-Phe-tRNAPhe (Pho) with Af DTD2. (E) Deacylation of N-ethyl-l-Phe-tRNAPhe (Pho) with Pho DTD2, Mj DTD2, and Af DTD2 showing no activity even at 500 nM enzyme concentration. (F) Deacylation of N-acetyl-d-Phe-tRNAPhe with both archaeal (Pho) and plant (At) DTD2s showing no activity even at 500 nM enzyme concentration. (G) Deacylation of N-acetyl-l-Phe-tRNAPhe with both archaeal (Pho) and plant (At) DTD2s showing no activity even at 500 nM enzyme concentration. (H) Co-occurrence of DTD2 with acetaldehyde biosynthesis in Archaea and plants.
