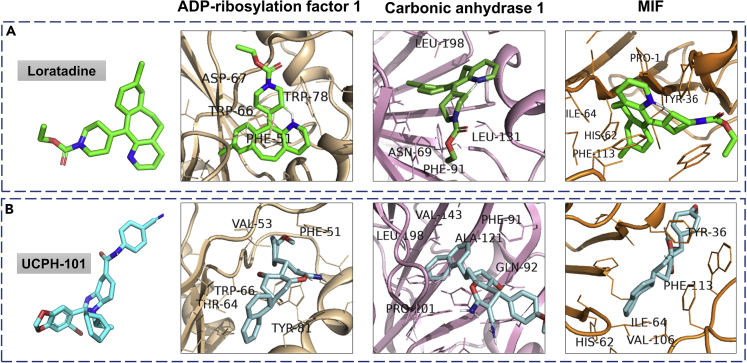
Figure 5.
Molecular docking studies of drugs binding to the host proteins involved in interleukin-12 signaling pathways
Autodock Vina (1.1.2) was used to identify the drugs binding to the host proteins involved in the neutrophil degranulation, translation, and interleukin pathway. A screening of 29 FDA-approved, 9 clinical, and 20 pre-clinical trial drugs against the host protein identified several potential drug candidates targeting the interleukin-12 signaling pathway.
(A) shows the drug Loratadine (green) docked with three proteins from the interleukin pathway; ADP-ribosylation factor 1 (binding energy or BE -9.8 kcal/mol), carbonic anhydrase 1 (BE -8.3 kcal/mol) and macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) (BE -8 kcal/mol).
(B) shows the same proteins docked with the drug UCPH-101 (cyan); ADP-ribosylation factor 1 (BE -9.9 Kcal/mol), carbonic anhydrase 1 (BE -8.5 kcal/mol) and MIF (BE -8.8 kcal/mol).
Both of the drugs bind to all three proteins with negative binding energy greater than their respective control inhibitor. The interacting amino acid residues, which are present on the ligand-binding pocket are labeled. Almost all of the interacting residues belong to hydrophobic amino acids.