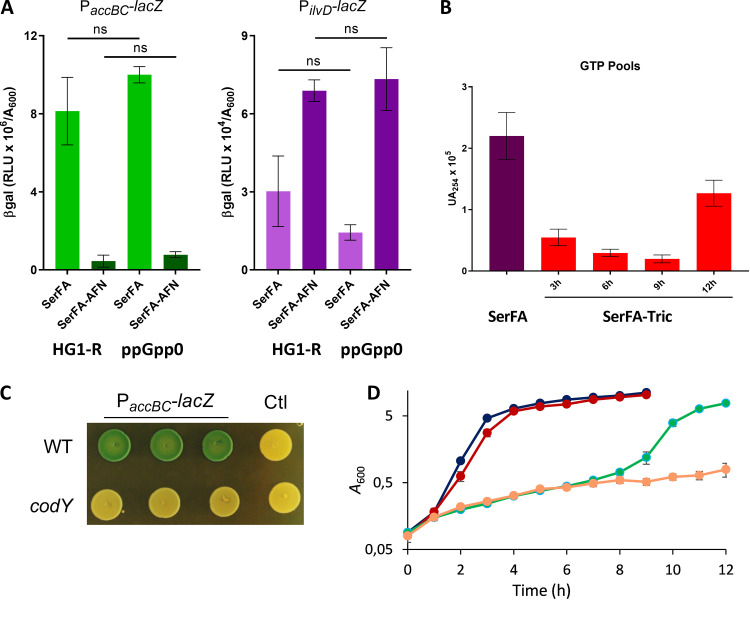
FIG 4.
GTP is depleted during anti-FASII latency phase. (A) PaccBC-lacZ (left) and PilvD-lacZ (right) sensor responses to anti-FASII latency were compared in S. aureus HG1-R and the (p)ppGpp null isogenic strain as indicated. β-Gal activities were measured after 3 h of incubation in SerFA and in medium containing the anti-FASII antibiotic AFN-1252. Data presented are means ± standard deviations from three biological replicates. P values were determined pairwise by Mann-Whitney; ns, not significant. (B) Newman strain GTP levels were assessed at different growth times during anti-FASII latency (3 h, 6 h, and 9 h) and outgrowth (12 h). Data presented are means ± standard deviations from duplicate independent experiments. (C) PaccBC-lacZ expression is lower in a codY mutant. USA300 and the codY derivative contained plasmids expressing PaccBC-lacZ or the control plasmid (pTCV-lac [Ctl]). Exponential-phase cultures issued from three independent colonies were adjusted to A600 = 0.1 and 5-μl drops were plated onto BHI plates containing erythromycin (5 μg/ml) and X-gal. Photographs were taken after 20 h at 37°C and 24 h at 4°C. (D) Growth rates of S. aureus USA300 and a confirmed codY mutant of the Nebraska mutant collection were compared in nonselective (SerFA) and SerFA-Tric conditions in four independent replicates. Black, WT in SerFA; red, codY in SerFA; green, WT in SerFA-Tric; orange, codY in SerFA-Tric. Mean and standard deviation are shown for each time point.