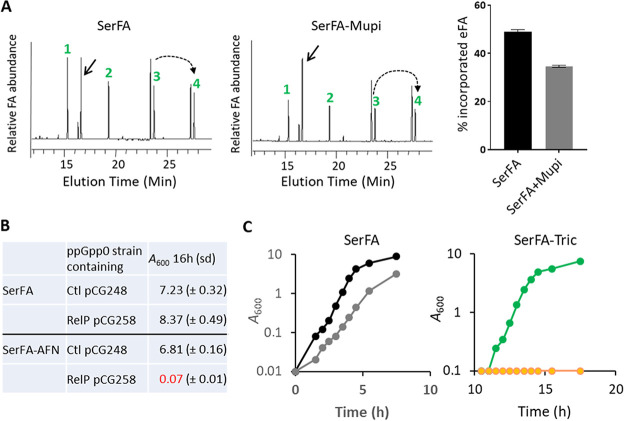
FIG 6.
Subinhibitory mupirocin inhibits S. aureus eFA incorporation in membrane phospholipids and synergizes with anti-FASII to inhibit adaptation. (A, left) Fatty acid profiles of S. aureus Newman grown in SerFA and SerFA+mupirocin (mupi). Samples were processed after 3 h growth. Black arrow, position of the main endogenous fatty acid ai15:0. Fatty acids (eFA) are as follows: 1, C14:0; 2, C16:0; 3, C18:1; and 4, C20:1 (elongation of C18:1). Dashed arrow, elongation of C18:1 (n + 2). (A, right) Percent eFA of Newman grown in SerFA without and with mupirocin, derived from integration of two fatty acid profiles from two independent experiments. (B) Control plasmid pCG248 and aTc-inducible relP-expressing plasmid pCG258 (26) were established in the ppGpp0 (null) strain. Strains were grown in SerFA and SerFA-AFN for 16 h in the absence of inducer. Anti-FASII adaptation is inhibited in the (p)ppGpp-expressing strain. (C) S. aureus Newman was grown in SerFA (black) and SerFA+mupi (gray) (left) or in SerFA-Tric (green) and SerFA-Tric+mupi (orange) (right). Growth was monitored by A600. Growth curves at right are shown starting at 10 h. Mupi was used at 0.05 μg/ml. Results are representative of three independent experiments.