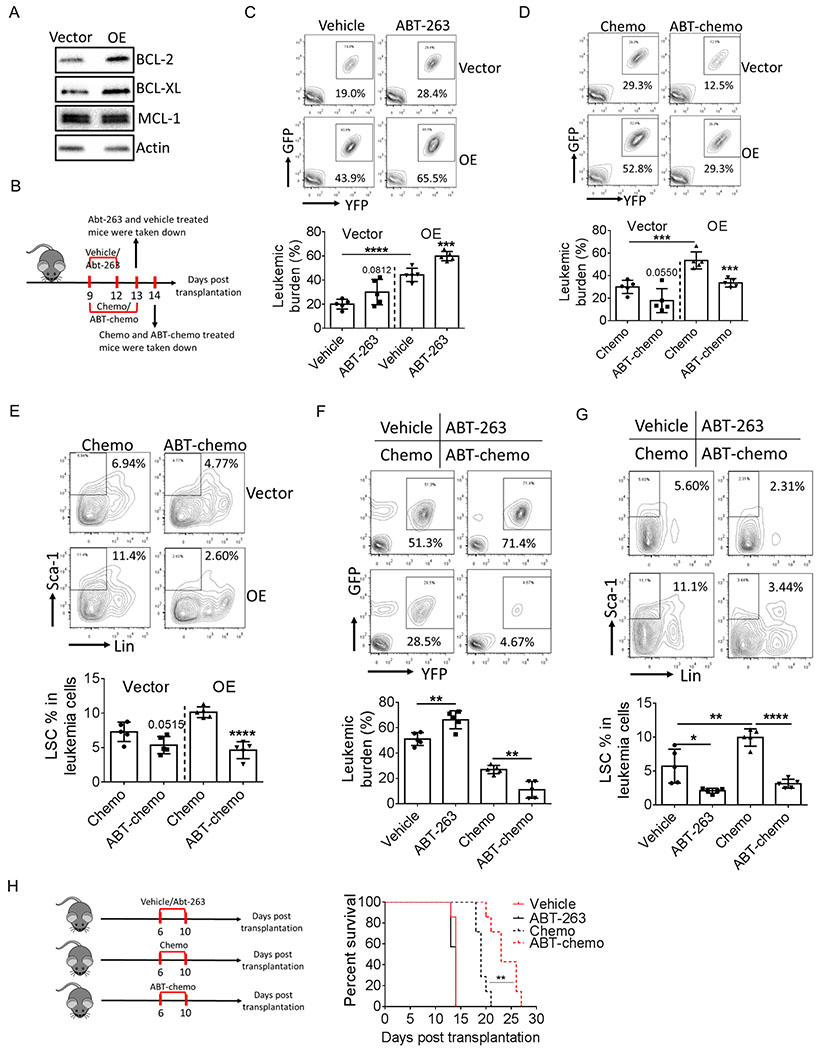
Figure 4.
LIPG regulates expression of BCL2 and BCL-XL.
A, Expression of anti-apoptotic proteins in vector-expressing and LIPG-OE lin− leukemia cells.
B, Schematic diagram for mice treatment.
C, BM leukemic burden in mice transplanted with vector-expressing or LIPG-OE bulk leukemia cells treated with vehicle or ABT-263 (50 mg/kg, p.o.) (n=5).
D-E, Mice were transplanted with vector-expressing or LIPG-OE bulk leukemia cells and treated with chemotherapy consisting of 5-day treatment of Ara-C (50 mg/kg, i.p.) and 3-day treatment of doxorubicin (1.5 mg/kg, i.p., first 3 days) or ABT-chemo therapy consisting of chemotherapy and ABT-263 (n=5). BM leukemic burden (D) and LSC percentage (E) were determined after therapy.
F-G, Mice transplanted with parental bulk leukemia cells were treated with chemotherapy or ABT-chemo therapy starting day 8 after transplantation. Liver leukemia burden (F) and LSC percentage (G) were determined at day 13 post transplantation (n=5).
H, Mice were transplanted with parental bulk leukemia cells and treated with vehicle, ATB-263, chemotherapy alone or ABT-chemo therapy. Survival of leukemic mice were monitored (n=7).
Error bars denote mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.005, ***p<0.0005 and ****p<0.00005.