Figure 1. Mechano-chemistry of S. pyogenes Cpa adhesin.
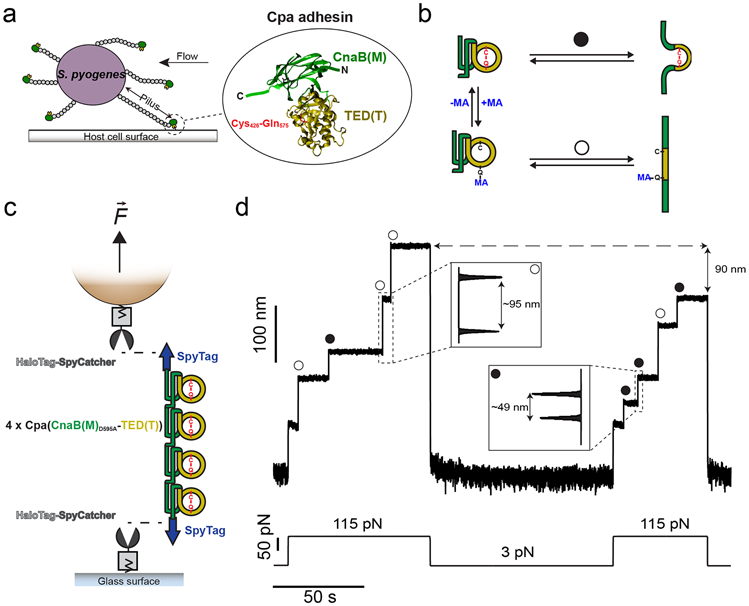
a) S. pyogenes attach to host cell surfaces through the Cpa protein, present in the tip-end of the pili. Cpa main core comprises the CnaB(M) domain (green), in whose fold the TED(T) domain is inserted (yellow). The TED(T) domain contains a thioester bond formed between the residues Cys426 and Gln575 (red), which mediates the attachment to cell-surface molecules. b) In the folded state, nucleophiles like methylamine (MA) can cleave the thioester bond and bind covalently to the Gln side chain (+MA); however, thioester bond reformation and ligand uncoupling (−MA) can occur. After mechanical extension, the presence (circle pathway) or absence (empty circle pathway) of the thioester bond can be assessed as a difference in the extension of the protein. c) Double-covalent magnetic tweezers experimental assay. Protein anchors SpyCatcher-HaloTag are covalently immobilized both to the surface of the glass and the paramagnetic bead. A chimeric polyprotein made of four copies of Cpa and flanked by SpyTag peptides is covalently linked to the glass and the bead through the reaction of the SpyCatcher/SpyTag split protein system. On the top of the scheme (not shown), the position of a pair of magnets is controlled for the application of calibrated forces to the tethered molecule. d) Magnetic tweezers recording of a Cpa polyprotein exposed to 100 mM methylamine, where the extension of the molecule is registered along time. A force pulse of 115 pN leads to the mechanical unfolding of the four Cpa domains, which is detected as stepwise increases in the extension. Here, three of the domains lack their internal thioester bond (empty circles) yielding an extension of ~95 nm, while one of the domains preserves its thioester bond (circle) and yields an unfolding extension of ~49 nm. Following a 100 s-long quench force pulse at 3 pN, which favors both folding and bond reformation, a second 115 pN pulse reveals that two Cpa domains reformed their thioester bonds (circles), decreasing the final extension of the polyprotein by 90 nm, as a consequence of the polypeptide sequence trapped by the newly formed bonds.
