Figure 3:
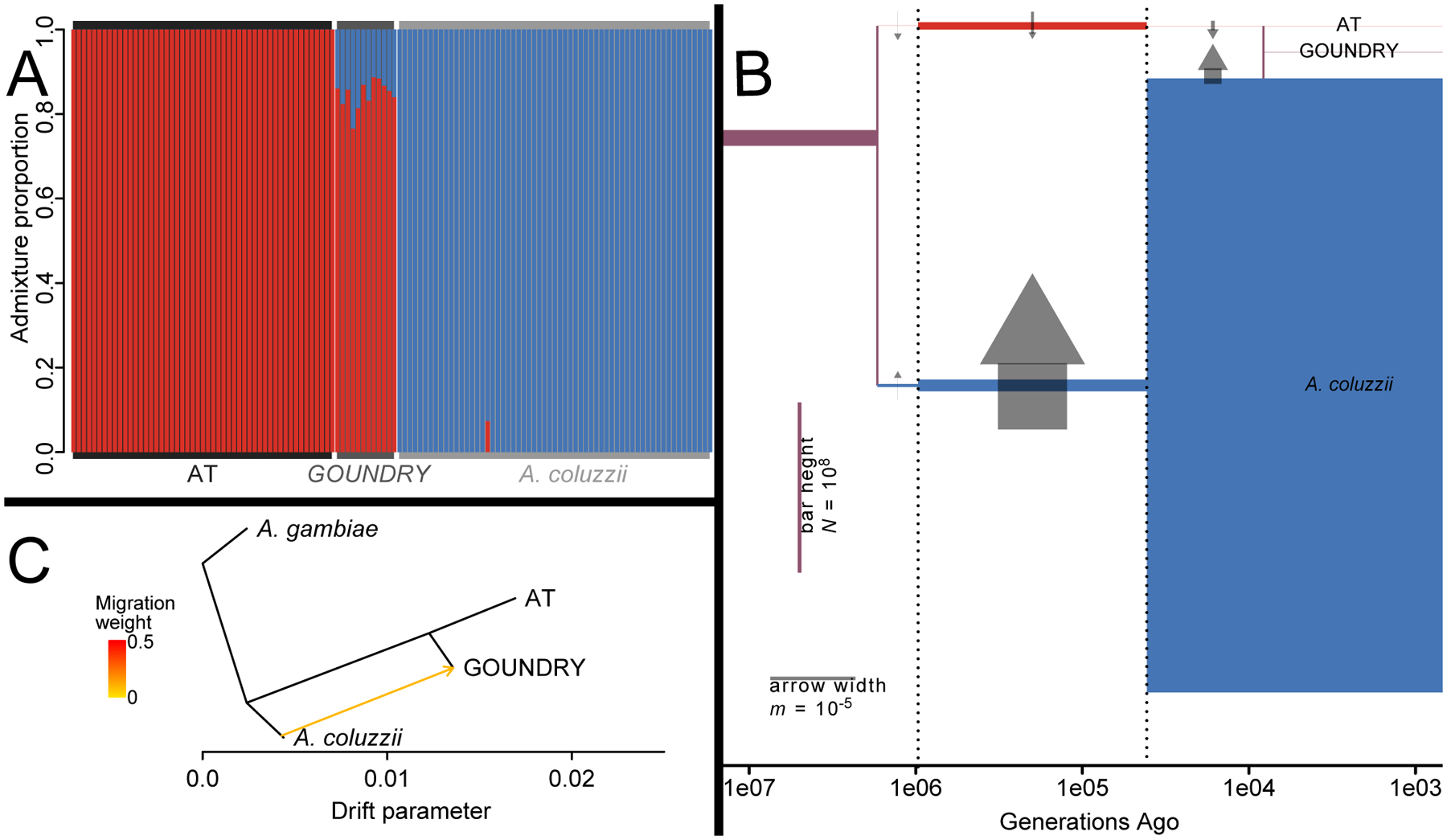
Relationships between AT, GOUNDRY, and A. coluzzii autosomes using jointly called genotypes. (A) Analysis with ADMIXTURE suggests two ancestral populations, closely approximated by contemporary AT and A. coluzzii, with GOUNDRY showing ancestry from both. (B) Analysis with dadi corroborates this model, with an AT/A. coluzzii split over one million generations ago, followed by ongoing gene flow and a recent admixed origin of GOUNDRY. Population sizes (heights of colored bars) and migration rates (widths of arrows) vary across three time periods (demarcated with dotted lines). (C) Analysis with TreeMix shows GOUNDRY as sister to AT but with in-migration from A. coluzzii.
