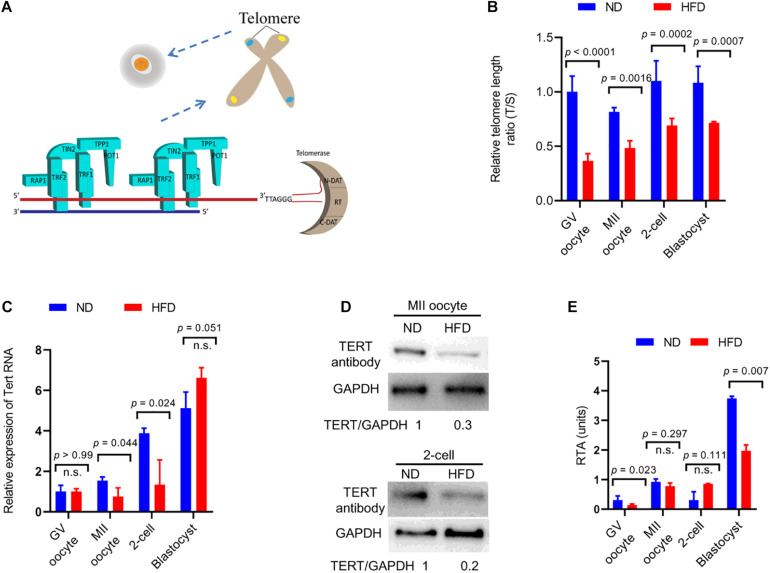
FIGURE 1.
Reduced telomere length in oocytes and embryos from obese mice. (A) Schematic diagram showing telomere structure, telomere-associated proteins, and telomerase in cells. Telomere and telomere-associated proteins include TRF1 (telomeric repeat binding factor 1), TRF2 (telomeric repeat binding factor 2), POT1 (protection of telomeres 1), TIN2 (TRF1-interacting nuclear protein-2), TPP1 (TIN2 interacting protein), and RAP1 (repressor-activator protein 1). Telomerase are composed of N-DAT (N-terminal domain), RT (DNA- and RNA-binding regions, a central catalytic reverse transcriptase domain), C-DAT (C-terminal domain). (B) Relative telomere length is expressed as a T/S ratio by quantitative real-time PCR analysis (n = 50 oocytes/embryos from 3 mice for each group). (C) The relative mRNA levels of Tert in GV/MII oocytes and 2-cell/blastocysts from ND and HFD mice were detected using qRT-PCR (n = 50 oocytes/embryos from 3 mice for each group). (D) The protein levels of TERT in MII oocytes and 2-cell embryos from ND and HFD mice were evaluated by Western Blot (n = 200 oocytes/embryos from 10 mice for each lane). GAPDH served as an internal control. (E) Relative telomerase activity (RTA) in GV/MII oocytes and 2-cell/blastocysts from ND and HFD mice was measured (n = 50 oocytes/embryos from 3 mice for each group). Data are expressed as mean percentage ± SD, of three independent experiments. A Student’s t-test was used for statistical analysis; n.s., not significant.