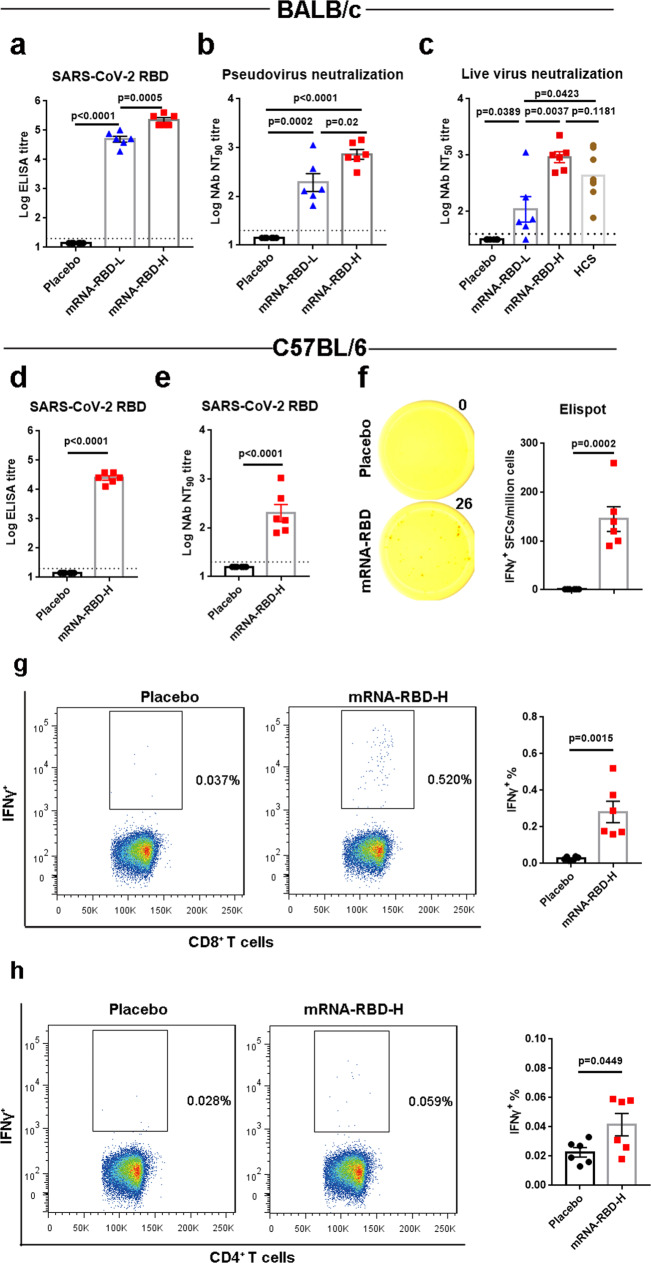
Fig. 2. Immunogenicity evaluation of a single mRNA-RBD vaccination.
a–c Groups of BALB/c mice (n = 6) were immunized with a single injection of mRNA-RBD at different doses or with a placebo via the i.m. route. Sera at 4 weeks post immunization were collected. SARS-CoV-2 RBD-specific IgG (a) and neutralizing antibody titers in sera against pseudovirus (b) and live virus (c) infection were determined. d–h C57BL/6 mice (n = 6) were inoculated with a single mRNA-RBD vaccination or a placebo. Serum samples were collected from mice at 4 weeks following vaccination. RBD-specific IgG titers and pseudovirus-neutralizing antibodies were measured as shown in d and e, respectively. f An ELISPOT assay was performed to evaluate the capacity of splenocytes to secrete IFNγ following re-stimulation with SARS-CoV-2 RBD peptide pools. g, h An ICS assay was conducted to quantify the proportions of IFNγ-secreting CD8+ (g) and CD4+ (h) T cells. mRNA-RBD-L indicates the low dose (2 μg). mRNA-RBD-H indicates the high dose (15 μg). HCS represents human convalescent sera. Data are means ± SEM (standard error of the mean). Comparisons were performed by Student’s t-test (unpaired, two tailed). Placebo animals = black circles; mRNA-RBD-L vaccinated animals = blue triangles; mRNA-RBD-H vaccinated animals = red squares; HCS = brown circles; dotted line = the limit of detection. Data are one representative result of two independent experiments. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.