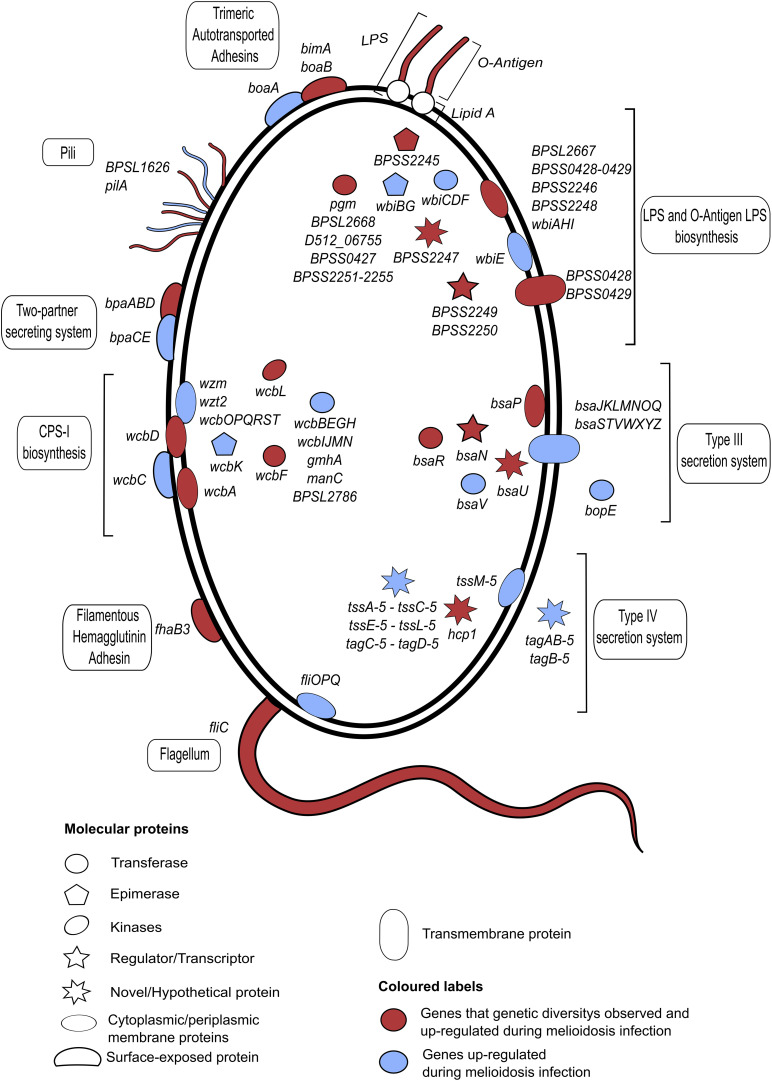
FIGURE 2.
A summary of B. pseudomallei genes or operons that are expressed during infection and characterized genetic variations. All plotted genes or operons are up-regulated during in vivo infections (Ooi et al., 2013), with a subset that reported genetic variations marked in red. The shape and location of each individual gene indicate the gene function and cellular compartment, respectively. All annotated genes or operons and their functions are described. The bacterium displays a repertoire of antigenic variations, including lipopolysaccharides (LPS), capsular polysaccharides (CPS) and surface proteins. B. pseudomallei LPS is immunologically classified into a number of serotypes A, B, and B2; with each serotype reported to be heterogeneously distributed across distinct geographical locations. Another highly diverse virulent protein is a fimbrial protein which displays a strong geographical distribution between Australia and Asia. Strains from Asia commonly possess a Yersinia-like fimbrial (YLF) gene cluster that believed to be horizontally acquired. B. pseudomallei carries 4 different types of CPS: CPS I, CPS II, CPS III, and CPS IV. A full gene description is provided in Supplementary Table 1.