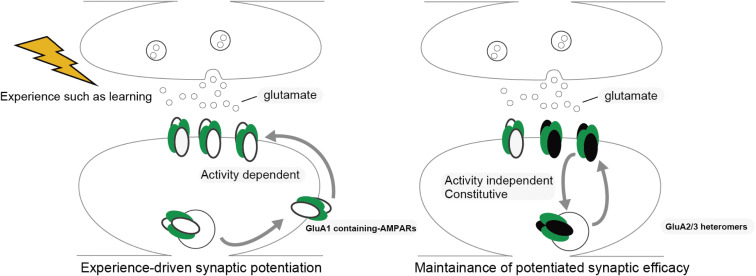
Figure 1.
Experience-dependent GluA1-containing AMPARs trafficking to the post-synaptic membrane. GluA1-containing AMPARs are trafficked to post-synaptic membranes in an experience-dependent manner, leading to the sustained potentiation of synaptic transmission, as is observed in LTP. GluA2/3 heteromers replace GluA1-containing AMPARs and are delivered to synapses in an experience-independent fashion, which maintains potentiated basal synaptic transmission.