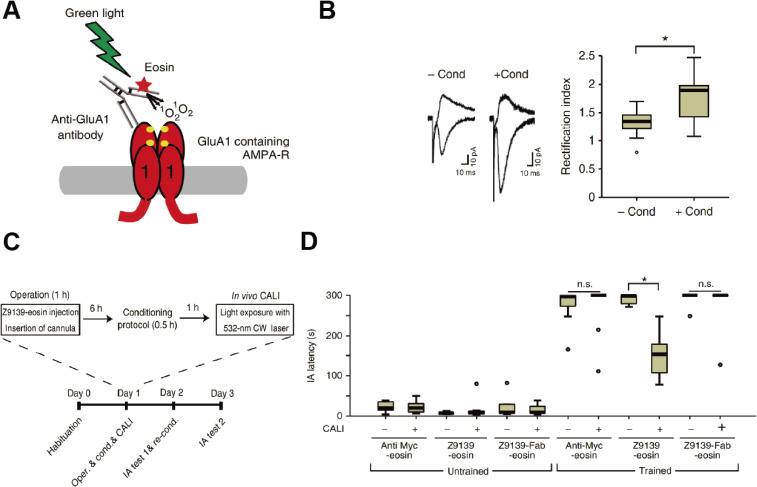
Figure 2.
In vivo CALI erases contextual fear memory. (A) Schematic representation of CALI for GluA1 using an anti-GluA1 monoclonal antibody (called Z9139) labeled with eosin, a photosensitizer. (B) IA learning increased the synaptic delivery of homomeric GluA1. Left: synaptic responses at the hippocampal CA3-CA1 synapses in acute brain slices obtained from animals with or without IA 1 h after conditioning. Right: average rectification index (the ratio of AMPA current of −60 mV to +40 mV) at hippocampal CA3-CA1 synapses with or without conditioning 1 h after IA learning. Note that the rectification index is increased at hippocampal CA3-CA1 synapses of animals with IA learning compared with those animals without. (C) Experimental procedure for in vivo CALI in combination with IA learning. (D) In vivo CALI with Z9139-eosin erased hippocampus-dependent fear memory. Latency for reentering the dark box in untrained mice or mice trained using the IA task. Animals were treated with Z9139-eosin, anti-Myc-eosin, or Z9139-Fab-eosin, with or without CALI. Note that the latency to reenter the dark box for trained mice treated with Z9139-eosin-CALI was shorter than those treated without CALI or with Myc-eosin-CALI. * P < 0.001. This derives from Ref. 31.