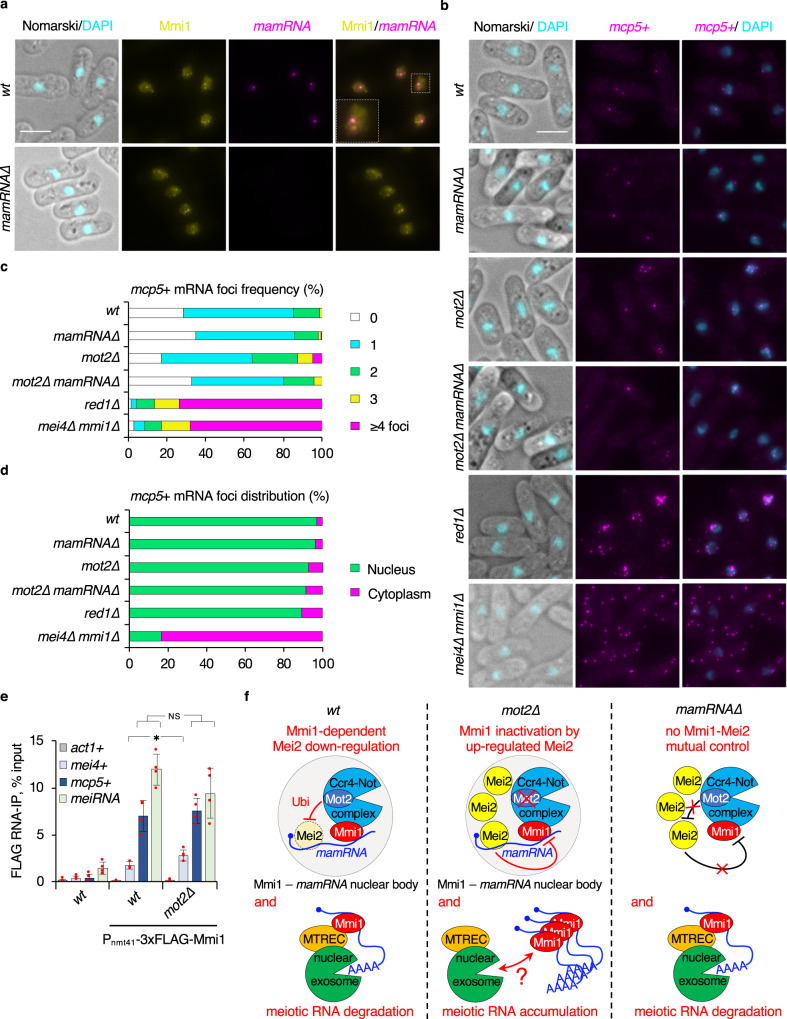
Fig. 4. Subcellular localization of Mmi1, mamRNA and meiotic mRNAs.
a, b Representative images of mamRNA (a) or mcp5 + mRNAs (b) detected by smFISH in cells of the indicated genetic backgrounds. DNA was stained with DAPI. In a, GFP-tagged Mmi1 was visualized in parallel. Images are shown as maximum-intensity projections of Z-stacks. White scale bars represent 5 µm. c, d Quantifications of smFISH analyses shown in b. c Distribution of mcp5 + mRNA foci frequency per cell (nwt = 1003 cells; nmamRNA∆ = 577; nmot2∆ = 824; nmot2∆mamRNA∆ = 240; nred1∆ = 839; nmei4∆mmi1∆ = 469). d Distribution of mcp5 + mRNA foci localization (nwt = 872 foci; nmamRNA∆ = 469; nmot2∆ = 1166; nmot2∆mamRNA∆ = 219; nred1∆ = 939; nmei4∆mmi1∆ = 1181). e Enrichments (% input; mean ± SD; n = 4) of act1 + , mei4 + , mcp5 + mRNAs and meiRNA upon pulldown of 2xFLAG-tagged Mmi1 in wt and mot2∆ cells. Student’s t test (two-tailed) was used to calculate p-values. Between Pnm41-3xFLAG-Mmi1 and mot2∆ Pnm41-3xFLAG-Mmi1, p = 0.02936 (mei4 + ) (0.05 > *>0.01); 0.62718 (mcp5 + ); 0.17136 (meiRNA). NS: not significant. Individual data points are represented by red circles. f Model depicting the role of mamRNA in the Mmi1–Mei2 mutual control in mitotic cells. In wt cells, Mmi1 binds to mamRNA to target Mei2 for downregulation by Mot2, which occurs in an Mmi1-containing nuclear body likely overlapping the mamRNA transcription site. This is required for efficient meiotic mRNA degradation by Mmi1, the Red1-containing MTREC complex and the nuclear exosome. In the absence of Mot2, increased Mei2 levels lead to meiotic mRNA accumulation in a mamRNA-dependent manner. Mmi1 inactivation occurs downstream of target recognition and nuclear retention. In mamRNA∆ cells, the Mmi1–Mei2 mutual control is abolished: Mei2 cannot be targeted to Mot2 but Mmi1 function in meiotic mRNA degradation is preserved.