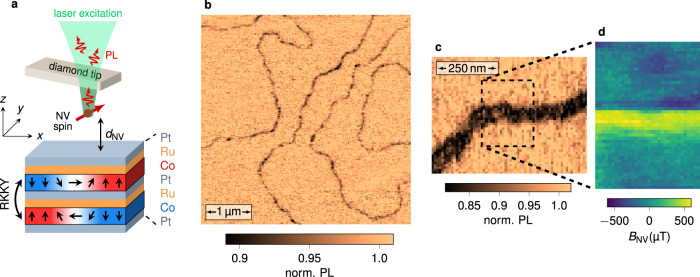
Fig. 2. All-optical imaging of domain walls in a synthetic antiferromagnet.
a Simplified sketch of the scanning-NV magnetometer and the SAF structure. The two magnetic Co layers are antiferromagnetically coupled through the Ru/Pt spacer layer by RKKY exchange interaction. The exact composition of the stack is Ta(10)/Pt(8)/Co(tCo)/Ru(0.75)/Pt(0.6)/Co(tCo)/Ru(0.75)/Pt(3), with the thicknesses in nm. The effective perpendicular magnetic anisotropy of the SAF is controlled by varying the Co thickness tCo. b PL quenching image recorded with the scanning-NV magnetometer above a SAF sample with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (tCo = 1.41 nm), showing an overview of the magnetic domain structure. c Closer view of a domain wall. d Static magnetic field distribution recorded above the area marked with the dashed rectangle in c. Only the component of the stray field along the NV quantization axis, BNV, is measured. This axis is defined by the spherical angles in the laboratory frame of reference (x, y, z).