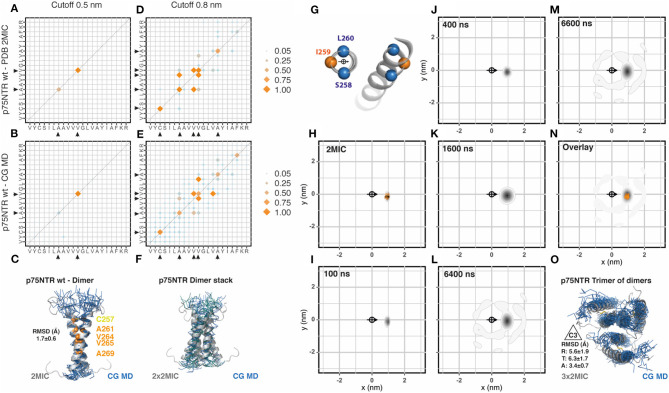
Figure 1.
p75NTR assembly. (A) Contact matrix of p75NTR wt NMR (PDB:2mic) at 0.5 nm cut-off distance. The amino acid sequence corresponds to residues V254 to R274. Black arrowheads indicate the residues involved in these interactions. Data corresponds to the averaged 10 NMR models. Scales correspond to the number of contacts normalized to the most frequent one [NCij/major(NCij)]. (B) Same as (A), for p75NTR coarse grained molecular dynamic (CG-MD) simulation. The analysis was performed on the full system (36x36) between 3 and 6 μs. (C) Alignment of the p75NTR NMR average model with a random p75NTR CG-MD dimer, together with the analysis of the averaged root mean square deviation (RMSD) of the alignment. (D) Same as (A), but using a cut-off distance of 0.8 nm. (E) Same as (B), but using a cut-off distance of 0.8 nm. (F) Example of stable interactions between dimers observed along the simulation, aligned to the reference structure 2 mic. (G) Residues chosen for the centroid and orientation vector used for radial distribution analysis. (H) Radial distribution analysis of p75NTR NMR structure 2mic, analyzed as coarse grained structure. The scale corresponds to the 2D-density function built from the scatter plot of XY-coordinates, as described in Methods. (I–M) Radial distribution analysis of different snapshots of p75NTR CG-MD at the indicated time points. (N) Overlay of the radial distribution of the reference structure (2mic, orange dots) and the CG-MD structures (gray density scale). (O) Example of a stable trimer of dimers found at early time points, assembled into the characteristic 3-fold symmetry axes C3, together with the averaged radial (R), tangential (T), and axial (A) RMSD.