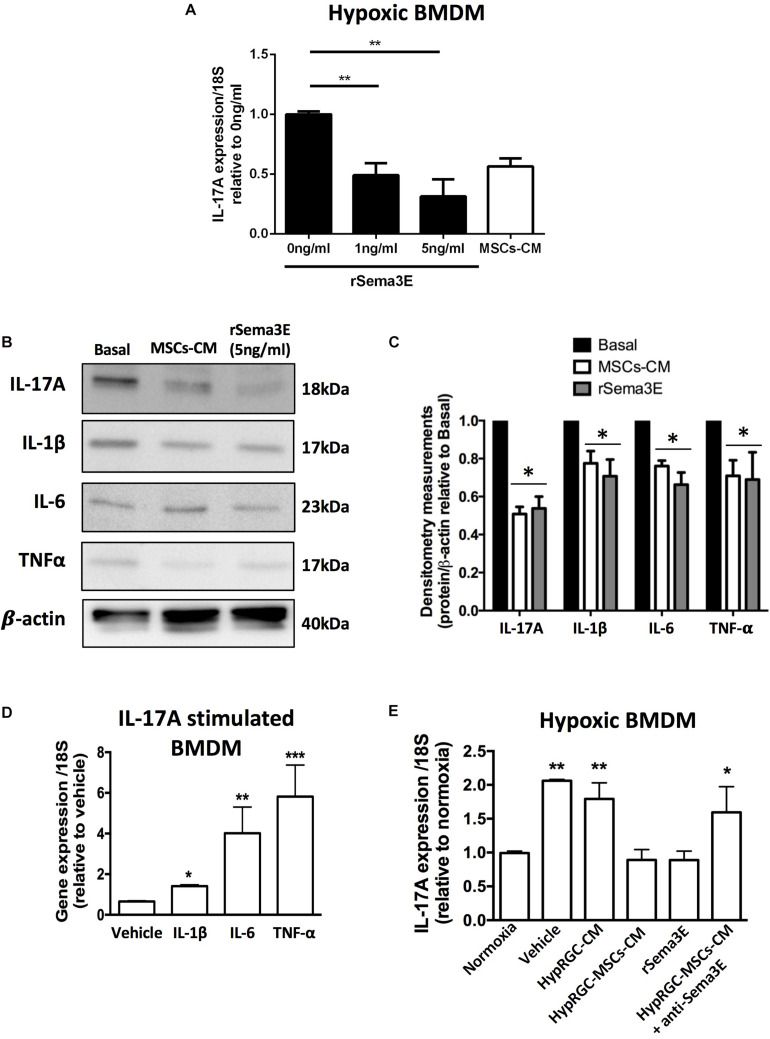
FIGURE 7.
rSema3E regulated myeloid cells-derived IL-17A in a dose-dependent manner. (A) Stimulation of hypoxic bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM) with rSema3E diminished IL-17A mRNA expression in a dose-dependent manner, while MSCs-CM have a partial effect (**p < 0.01 vs 0 ng/Sema3E, values are mean ± SEM, n = 6). (B) Representative images from Western blot analysis of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-17A, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α) in hypoxic BMDM treated with MSCs-CM and rSema3E (5 ng/ml) showing reduced protein levels of the cytokines with rSema3E and MSCs-CM treatments in comparison to vehicle. β-actin was used as internal control. (C) Densitometry quantification at right (* < 0.05 vs Basal, values are mean ± SEM n = 3 independent experiments, pool of 2 wells per group). (D) Stimulation of hypoxic BMDM with rIL-17A (100 ng/ml) increases IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α mRNA expression (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs vehicle, values are mean ± SEM, n = 3). (E) Real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) analysis of bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM) pre-exposed to hypoxia (5% O2) showing the augmented BMDMs-derived IL-17A expression in vehicle (DMEM alone) and hypoxic RGC conditioned media (HypRGC-CM) treatments after 24 h of incubation. BMDMs treated with the conditioned medium derived from RGCs previously stimulated with MSCs-CM (HypRGC-MSCs-CM) strongly supressed (p < 0.01) the mRNA levels of IL-17A in a similar way to the supplementation with the rSema3E (5 ng/ml). The anti-inflammatory effect of HypRGC-MSCs-CM was abrogated in the presence of a neutralizing antibody against Sema3E (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, vs normoxia, values are mean ± SEM, n = 3).