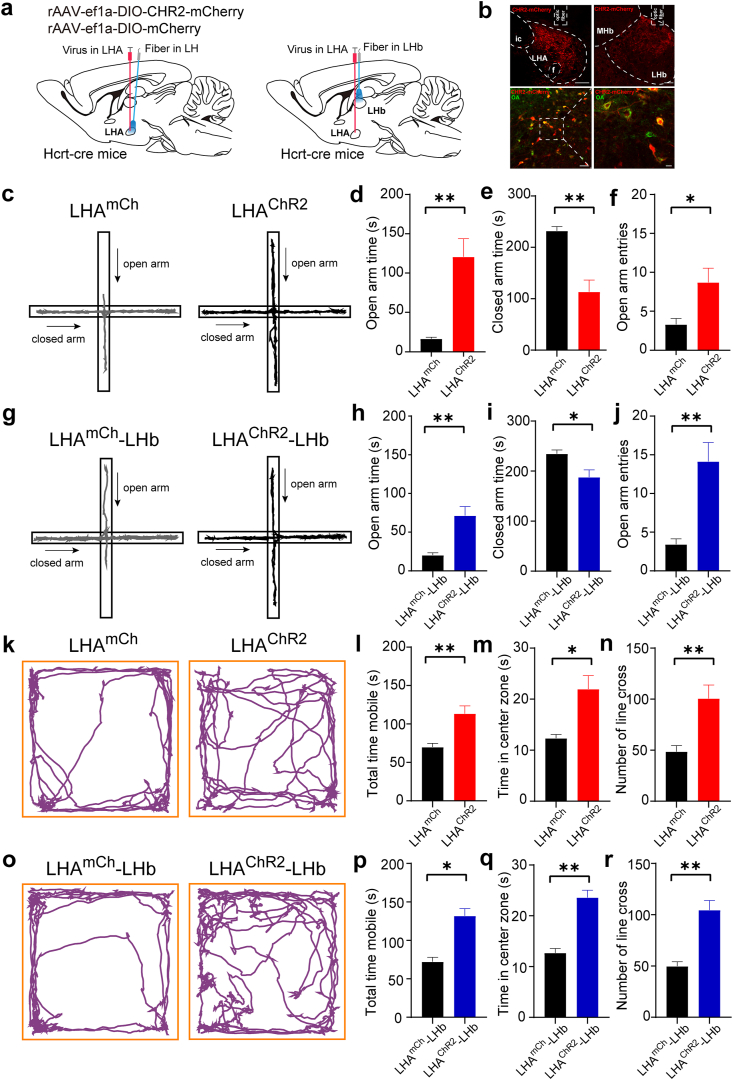
Fig. 5.
Optogenetic activation of the LHAOrx-LHbGlu circuit relieved anxiety-like behaviors after chronic social defeat stress
(a) Schematic diagram of virus injection and fiber implantation into the LHA (LHAmCh represents the mCherry control group and LHAChR2 represents the optogenetic activation group) or the LHb (LHAmCh-LHb represents the control group and LHAChR2-LHb represents the optogenetic activation group) of the Hcrt-cre mice. (b) Representative images of virus expression and optical fiber placement. (c) Representative trajectories of LHAmCh and LHAChR2 mice in the elevated plus maze test. (d) Time spent in the open arms during optogenetic activation of LHAmCh and LHAChR2 (16.41 ± 2.084 s vs. 120.8 ± 23.04 s, t = 4.511, p = 0.0007). (e) Time spent in the closed arms with optogenetic activation of LHAmCh and LHAChR2 (232.0 ± 8.361 s vs. 113.7 ± 22.63 s, t = 4.906, p = 0.0002). (f) Number of entries into the open arms during optogenetic activation of LHAmCh and LHAChR2 (3.286 ± 0.7781 vs. 8.714 ± 1.809, t = 2,757, p = 0.0174). (g) Representative trajectories of LHAmCh-LHb and LHAChR2-LHb mice in the elevated plus maze test. (h) Time spent in the open arms with optogenetic activation of LHAmCh-LHb and LHAChR2-LHb (20.19 ± 3.270 s vs. 71.49 ± 11.53 s, t = 4.280, p = 0.0011). (i) Time spent in the closed arms during optogenetic activation of LHAmCh-LHb and LHAChR2-LHb (234.7 ± 7.556 s vs. 187.9 ± 14.60 s, t = 2.850, p = 0.0128). (j) Number of entries into the open arms during optogenetic activation of LHAmCh-LHb and LHAChR2-LHb (3.429 ± 0.7190 vs. 14.14 ± 2.444, t = 4.206, p = 0.0012). (k) Representative trajectories of LHAmCh and LHAChR2 mice in the open field test. (l) Total mobile time in the open field during optogenetic activation of LHAmCh and LHAChR2 (69.90 ± 4.800 s vs. 113.4 ± 10.23 s, t = 3.592, p = 0.0058). (m) Time spent in the center zone of the open field during optogenetic activation of LHAmCh and LHAChR2 (12.34 ± 0.7521 s vs. 21.97 ± 2.647 s, t = 3.204, p = 0.0108). (n) Number of line crossings in the open field during optogenetic activation of LHAmCh and LHAChR2 (48.60 ± 5.810 vs. 100.5 ± 13.33, t = 3.319, p = 0.0090). (o) Representative trajectories of LHAmCh-LHb and LHAChR2-LHb mice in the open field test. (p) Total mobile time in the open field during optogenetic activation of LHAmCh-LHb and LHAChR2-LHb (72.20 ± 5.798 s vs. 131.9 ± 9.382 s, t = 5.136, p = 0.0006). (q) Time spent in the center zone of the open field during optogenetic activation of LHAmCh-LHb and LHAChR2-LHb (12.70 ± 0.8678 s vs. 23.60 ± 1.438 s, t = 6.152, p = 0.0002). (r) Number of line crossings in the open field during optogenetic activation of LHAmCh-LHb and LHAChR2-LHb (49.80 ± 4.420 vs. 104.5 ± 9.451, t = 4.891, p = 0.0009). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (unpaired t-test). LHA, lateral hypothalamic area; LHb, lateral habenula.