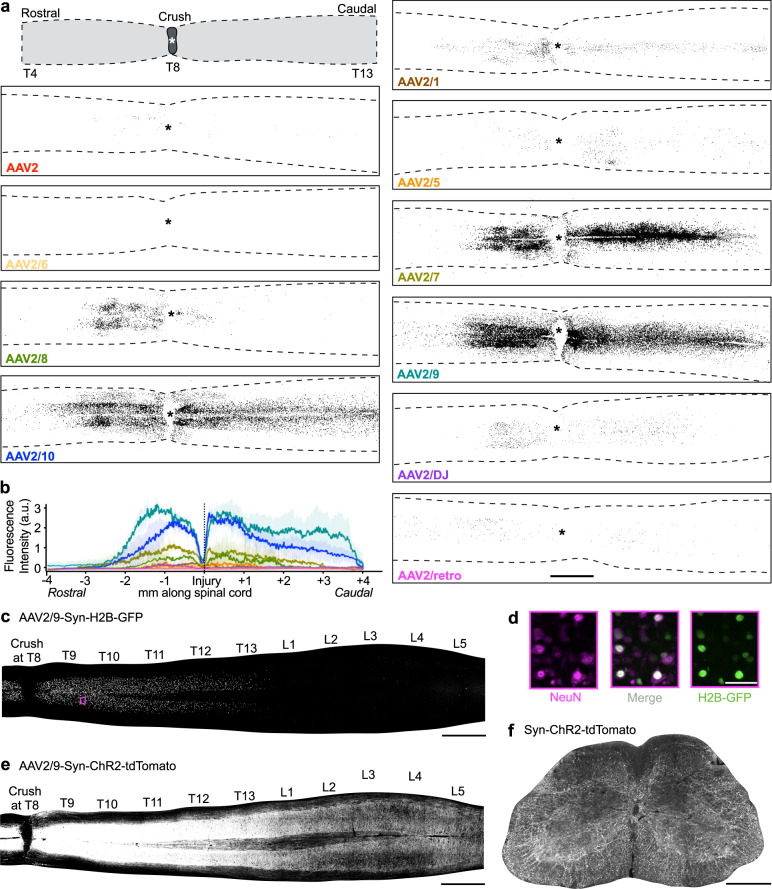
Fig. 1. A screen for AAV serotypes that are able to cross blood spinal cord barrier and transduce cells around the lesion after spinal cord crush.
a Representative images of longitudinal sections of the thoracic spinal cord show transduced cells after tail vein injection of different serotypes of AAVs expressing CAG-H2B-GFP at 3 h after T8 crush injury. Similar distributions were observed in all of 3 analysed mice for each AAV serotype. Scale bar: 1 mm. An asterisk represents lesion centre. b Quantification of GFP expression along the longitudinal axis. Mean ± SD are indicated by line and shadow with corresponding colours. a.u.: arbitrary unit. The fluorescence intensities were normalized to that in AAV2/9 (n = 3 mice for each AAV serotype, 5 sections per mouse). c Representative image showing the expression of H2B-GFP (cell bodies only) in different spinal levels. Similar distributions were observed in all of 3 analysed mice. Scale bar: 1 mm. d Magnification of the highlighted area one spinal segment away from the lesion (purple box in (c)), indicating co-localization of H2B-GFP and NeuN. Scale bar: 100 µm. e Representative image showing the expression of ChR2-tdTomato (cell bodies and axons) in different spinal levels. Similar distributions were observed in all of 3 analysed mice. Scale bar: 1 mm. f Cross section of the lumbar spinal cord showing descending ChR2-tdTomato+ axons from thoracic propriospinal neurons. Similar distributions were observed in all of 3 analysed mice. Scale bar: 500 µm.