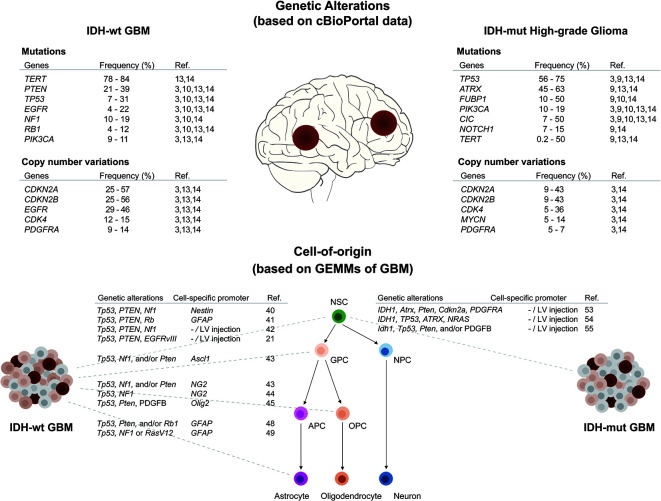
Figure 1.
Overview of genetic alterations and cell-of-origin in IDH-wildtype and IDH-mutant GBMs. (Upper panel) Frequently occurring driver mutations and CNVs in IDH-wildtype and IDH-mutant high-grade gliomas (WHO grade 3 & 4) were listed as above. The frequencies were obtained from published data using cBioPortal (19, 20). (Lower panel) Multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) have capability to self-renewal and differentiate into progenitors with restricted potential including glial precursor cells (GPCs), oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs), astrocyte precursor cells (APCs), and neural progenitor cells (NPCs). Using specific genetic alterations and cell-specific promoters, NSCs and progenitor cells can be transformed to generate either IDH-wildtype or IDH-mutant GBMs in GEMMs.