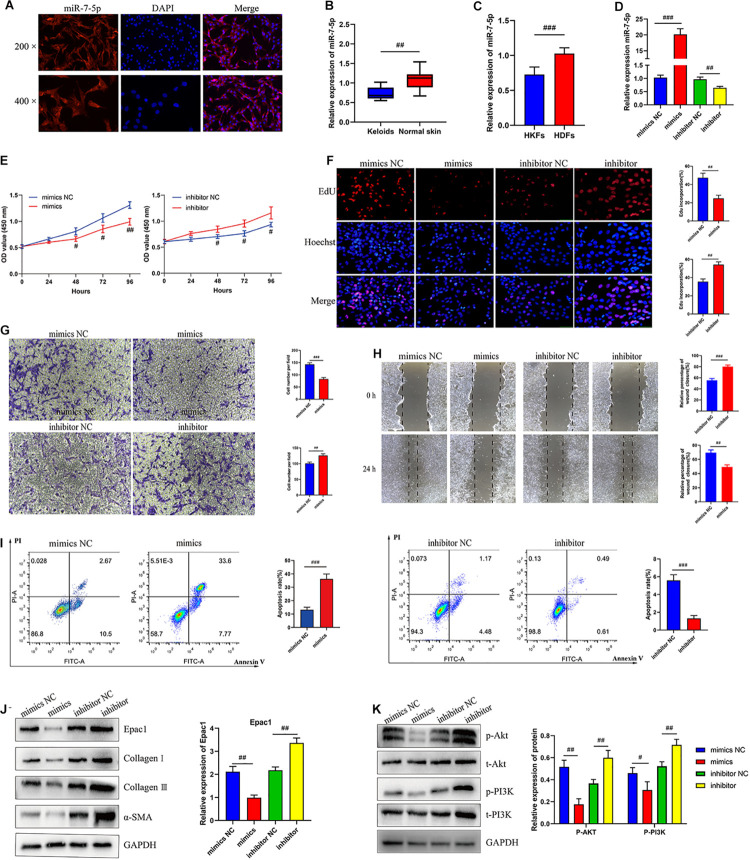
FIGURE 3.
MiR-7-5p regulated HKFs proliferation, migration, apoptosis, and ECM deposition in vitro by targeting Epac1. (A) FISH assays were performed to observe the cellular location of miR-7-5p (red) in HKFs (magnification, 200× and magnification, 400×). (B) The relative RNA levels of miR-7-5p were evaluated by qRT-PCR between keloid tissues and normal skin. (C) The relative RNA levels of miR-7-5p were evaluated by qRT-PCR between HKFs and HDFs. (D) The transfection efficiency of miR-7-5p was evaluated by qRT-PCR in HKFs transfected with the miR-7-5p mimics or inhibitor, respectively. (E) CCK-8 assays and (F) EdU assays were performed to evaluate the proliferation ability in HKFs transfected with the miR-7-5p mimics or inhibitor, respectively. Magnification, 200×. (G) Transwell migration assays (magnification, 200×) and (H) wound healing assays (magnification, 20×) were applied for assessing the migration ability of HKFs transfected with the miR-7-5p mimics or inhibitor, respectively. (I) Cell apoptosis was examined using flow cytometry. (J,K) The protein levels of Epac1, collagen I, collagen III, α-SMA, and the protein phosphorylation levels of Akt and PI3K in HKFs transfected with miR-7-5p mimics or inhibitor by western blot assays. Data was shown as mean ± SD. ns indicated no significance, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, vs. NC.