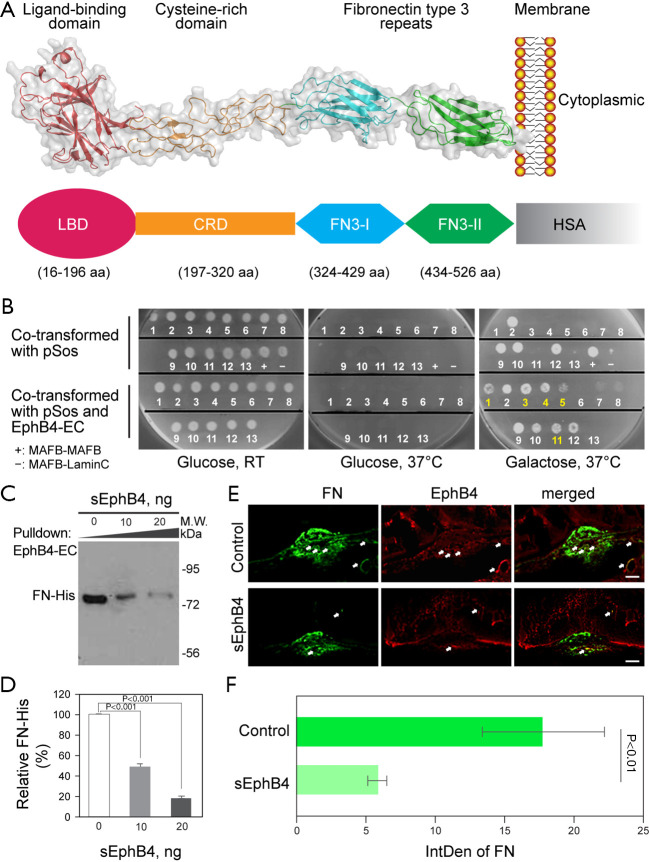
Figure 1.
Human EphB4 extracellular domain and the interaction of EphB4 and FN (fibronectin). (A) Diagram of human sEphB4 extracellular domain (EphB4-EC) and soluble sEphB4-HSA (sEphB4-HSA). Top, sEphB4 (human EphB4 extracellular domain) with a ligand binding globular domain (LBDG), a cysteine rich domain (CRD), and two fibronectin type FN 3-like domains (FFN3-I and FN3-II). Bottom, sEphB4-HSA that has human serum albumin (HSA) fused to the C-terminus of human EphB4-ECsEphB4. (B) Interaction of EphB4 with FN. Interaction partners of EphB4 extracellular domain (B4-EC) were identified using CytoTrap yeast two-hybrid system. The positive clones were co-transformed with B4-EC to validate their interaction. The validated clones can grow at 37 °C on galactose containing (SG) plate only in the presence of B4-EC co-expression. Among the five validated positive clones, #1, 4, 5, and 11 are FN clone variants, whereas #3 is a different gene. (C,D) Recombinant B4-EC was biotinylated and immobilized on streptavidin beads, followed by incubation with recombinant His-tagged FN (FN-His) at presence of 0, 10, and 20 ng sEphB4. After wash with PBS, the bound FN-His was detected with anti-His tag antibody on Western, and the relative density of FN-His was shown in (D). The double labeling of FN and EphB4 in the laser induced CNV (days 14, E), green indicates the positive staining of FN and red represents EphB4 immunoreactivity. Yellow is the colocalization of FN and EphB4 (arrows). The intensity of FN staining was significantly reduced in the CNV (choroidal neovascularization) lesion injected with sEphB4-HSA compared with PBS (phosphate-buffered saline) injection (F). Scale bar: 50 µm.