Figure 2. NADPH oxidase activity and hPMN cell death.
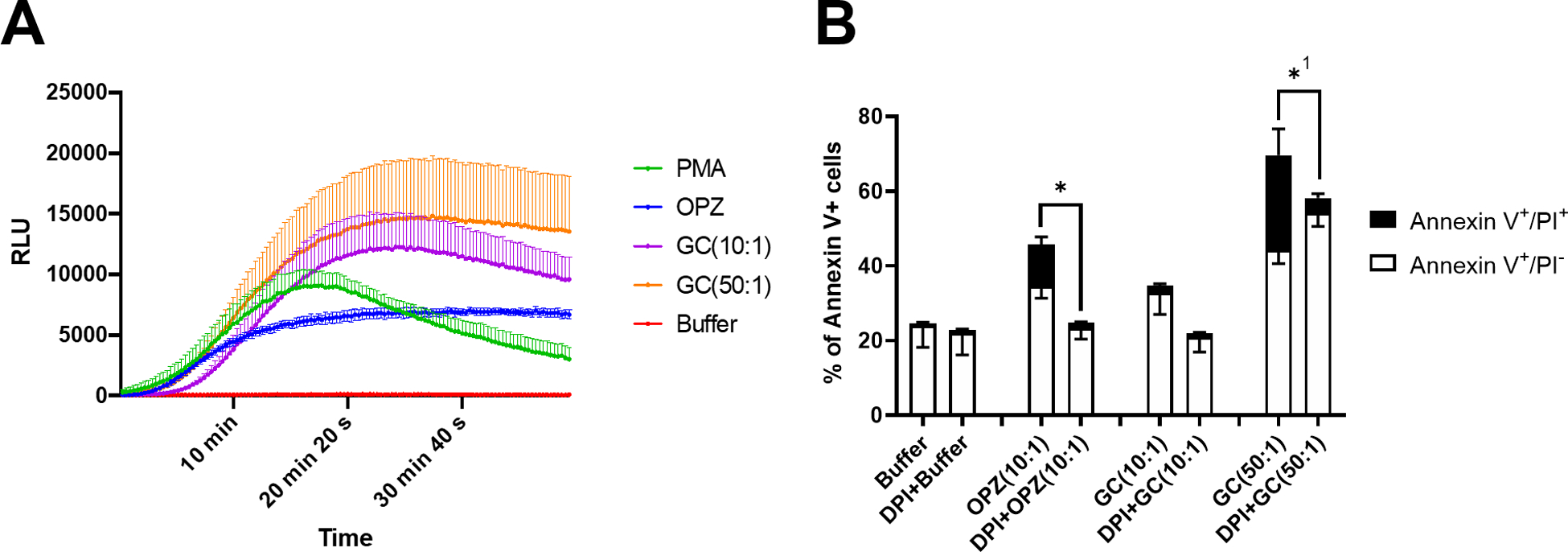
(A) The NADPH oxidase activity of hPMN was assessed by monitoring luminol-enhanced chemiluminescence of stimulated cells. The soluble agonist PMA was used as a positive control for oxidase activity. Both OPZ (10:1 MOI) and GC triggered oxidant production and the response to GC was dose dependent. (B) At 2 hours after phagocytosis in DPI-treated hPMN, the percent of Annexin V+/PI− and Annexin V+/PI+ cells in OPZ-fed hPMN were less than those fed OPZ without DPI treatment. Although DPI treatment did not significantly reduce Annexin or PI positivity of hPMN fed GC at 10:1 MOI, reduction in Annexin V+/PI+ cells was statistically significant at 50:1 MOI GC. Bars represent the average ± SEM from three independent experiments. p-values were determined using a two-way ANOVA and Turkey’s posttest (* p < 0.05). 1 denotes statistical significance in Annexin V+/PI+ population, and not in Annexin V+/PI−.
