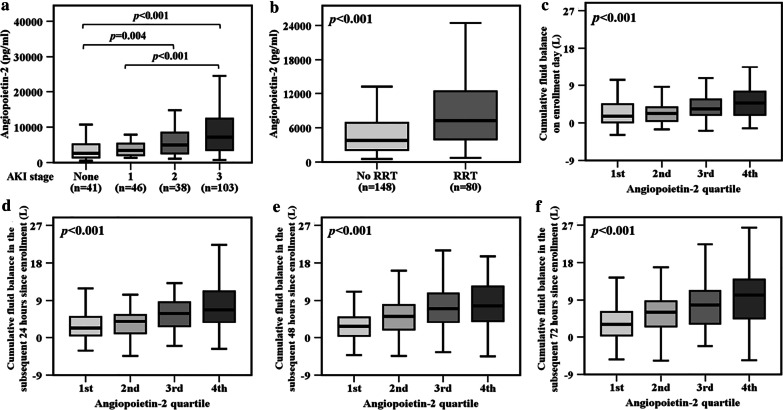
Fig. 3.
a Plasma angiopoietin-2 levels were significantly associated with severity of AKI. b Patients requiring renal replacement therapy (RRT) had significantly higher plasma angiopoietin-2 levels than those not requiring RRT during hospitalization. Higher plasma angiopoietin-2 levels by quartile were significantly associated with positive fluid balance c on enrollment day, d in the subsequent 24 h, e 48 h and f 72 h since enrollment. Data in panels a–f were summarized as boxplots where box encompassed 25‒75th percentile, error bars encompassed 10‒90th percentile and horizontal line showed median. Groups were compared by Kruskal–Wallis test (panels a and c–f) or Mann–Whitney U test (panel b). Post hoc analysis of groups comparison was performed using Mann–Whitney U test and Bonferroni correction (panel a)