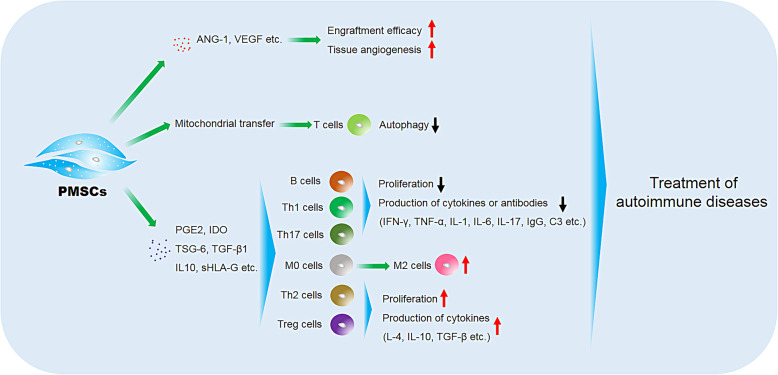
Fig. 2.
The main mechanisms of PMSCs for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. PMSCs can suppress the function of B and T cells and decrease the proportion of Th1/Th2, Th17/Treg, and M1/M2 via secreting IDO, PGE2, TSG-6, TGF-β1, IL10, sHLA-G, etc. Furthermore, PMSCs can downregulate the levels of inflammatory cytokines as IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IL-17, and the like, but upregulate the levels of IL-4, IL-10, and TGF-β in the serum or target tissues after transplantation. Moreover, PMSCs can secrete various growth factors such as VEGF and ANG-1 to enhance the therapeutic effects