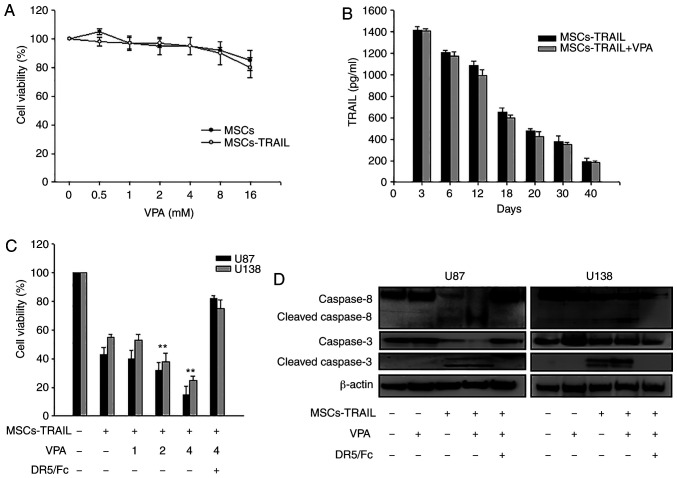
Figure 3.
Effect of VPA treatment on MSCs-TRAIL. (A) MSCs and MSCs-TRAIL were treated with VPA (0-16 mM) and their viability was determined using a MTT assay. (B) After VPA (2 mM) was added to MSCs or MSCs-TRAIL, the concentration of secreted TRAIL in culture supernatant was analyzed via ELISA on the indicated day. (C) Glioma cells (U87 and U138) were treated with VPA (0–4 mM) with MSCs-TRAIL with or without DR5/Fc chimera protein (100 ng/ml), and then the viability of glioma cells was determined using a MTT assay. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. **P<0.01 in the comparison of alone treatment with untreated control; as compared with the treatment with VPA or MSCs-TRAIL alone (one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni multiple comparison test). (D) Glioma cells (U87 and U138) were treated with VPA (2 mM), MSCs-TRAIL or VPA and MSCs-TRAIL with or without DR5/Fc chimera protein (100 ng/ml). After 24 h, total cell extracts were analyzed using western blotting with antibodies against caspase-8 (upper panel) and caspase-3 (bottom panel). The relative expression of each protein was normalized to β-actin. Each western blot test was conducted on different parts using same gel and exposure. VPA, valproic acid; TRAIL, tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; DR, death receptor; MSCs-TRAIL, tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-secreting human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.