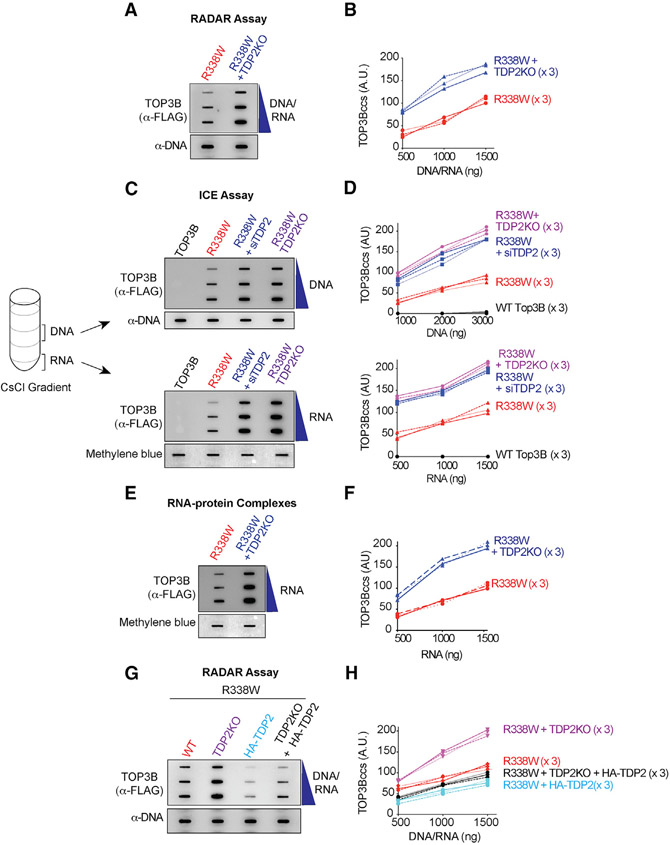
Figure 2. TDP2 Excises Cellular TOP3Bccs from Both DNA and RNA.
(A) WT or TDP2KO HCT116 cells were transfected with R338W-TOP3B. After 72 h, protein-nucleic acid adducts were isolated by RADAR assay. Slot-blotted TOP3Bccs were detected with anti-FLAG antibody. Loading was tested by slot blotting and probing with anti-dsDNA antibody.
(B) Quantitation of TOP3Bccs from three independent experiments as shown in (A). TOP3Bccs were measured by densitometric analyses of slot-blot signals and plotted as a function of total nucleic acid (DNA and RNA) concentration.
(C) HCT116 WT and TDP2KO cells were transfected with WT-TOP3B or R338W-TOP3B and siTDP2 constructs as indicated. After 72 h, ICE bioassays were performed to isolate DNA and RNA fractions. TOP3Bccs were detected with anti-FLAG antibody. Loading was tested with anti-dsDNA antibody or methylene blue staining (RNA).
(D) Quantitation of TOP3Bcc in three independent experiments as shown in (C).
(E) WT and TDP2KO HCT116 cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged R338W-TOP3B. After 72 h, protein-RNA adducts were isolated using TRIzol. TOP3Bccs were detected with anti-FLAG antibody. Loading was tested by methylene blue staining.
(F) Quantitation of TOP3Bcc in RNA in three independent experiments as shown in (E).
(G) Ectopic expression of TDP2 reduces TOP3Bccs. WT and TDP2KO HCT116 cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged R338W-TOP3B alone or co-transfected with HA-tagged TDP2. After 72 h, TOP3Bccs were detected with anti-FLAG antibody. Loading was tested with anti-dsDNA antibody.
(H) Quantitation of TOP3Bccs in three independent experiments as shown in (G).
See also Figure S2.