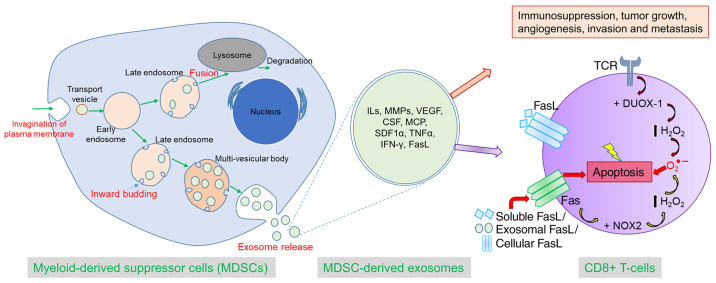
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram showing the process of biogenesis of exosomes from MDSCs and the role of MDSC-derived exosomes in tumor progression and immunosuppression by AICD. Exosomes secreted from the MDSCs contain pro-tumorigenic factors from the parent cells and can play a crucial role in immunosuppression, tumor growth, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis by dispensing their contents into the other TME cells or distant cells. MDSC-derived exosomes can activate CD8+ T-cells, and TCR triggering causes activation of DUOX-1 that leads to H2O2 production and eventually generation of ROS in mitochondria. Prolonged TCR stimulation triggers overexpression of both Fas (receptor) and FasL (ligand), which culminates in fratricide (from direct cell contact) or autocrine suicide (interaction of soluble FasL with Fas).