Figure 5.
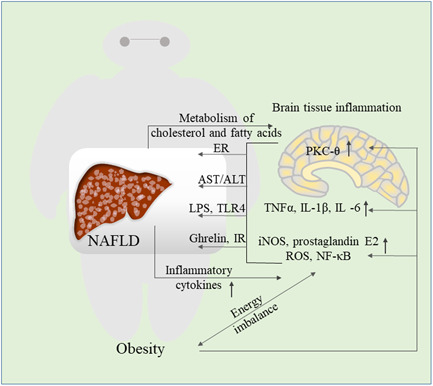
The relationship between obesity‐induced brain tissue inflammation and NAFLD. Overnutrition caused by obesity activates NF‐κB, pro‐inflammatory cytokines, PKC‐θ and other signaling pathways in the brain. Following inflammation of the brain tissue, endoplasmic reticulum stress occurs, AST/ALT increases, and LPS stimulates TLR4 signals, ghrelin induces insulin resistance and promotes liver lipid accumulation. The progress of NAFLD is also accompanied by an increased inflammatory cytokines profile in the brain, at the same time, the metabolism of cholesterol and fatty acids in the brain is unbalanced, which further aggravates the brain tissue inflammation. ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; IR, insulin resistance; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NF‐κB, nuclear factor‐κB; PKC‐θ, protein kinase C‐θ; ROS, reactive oxygen species
