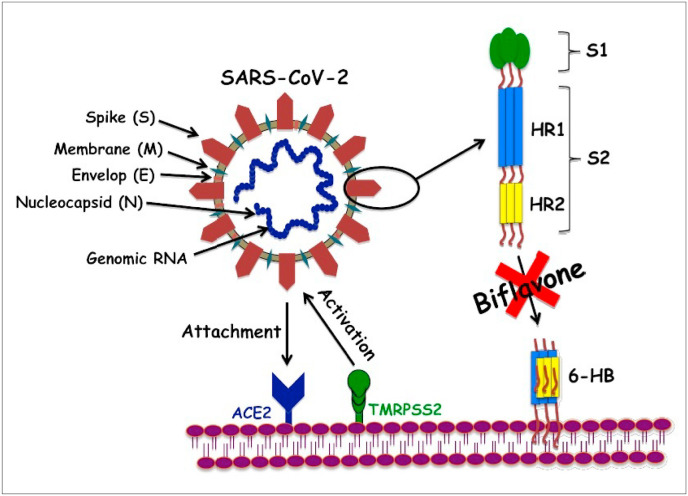
Scheme 2.
Schematic representation of the plausible route of naturally occurring biflavones, hinokiflavone (3) and robustaflavone (4) mediated inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 S protein attack on human ACE2 receptors. During the process of virions attachment to the receptors, type-2 transmembrane protease (TMPRSS2) cleaves the S proteins from ACE2 leading to the activation of the S proteins. HR1 and HR2 regions of S2 protein of SARS-CoV-2 interactions with ACE2 receptors instigating six-helix bundle core fusion structure (6-HB) formations is blocked by biflavones and hence, inhibition of membrane fusion can be achieved.