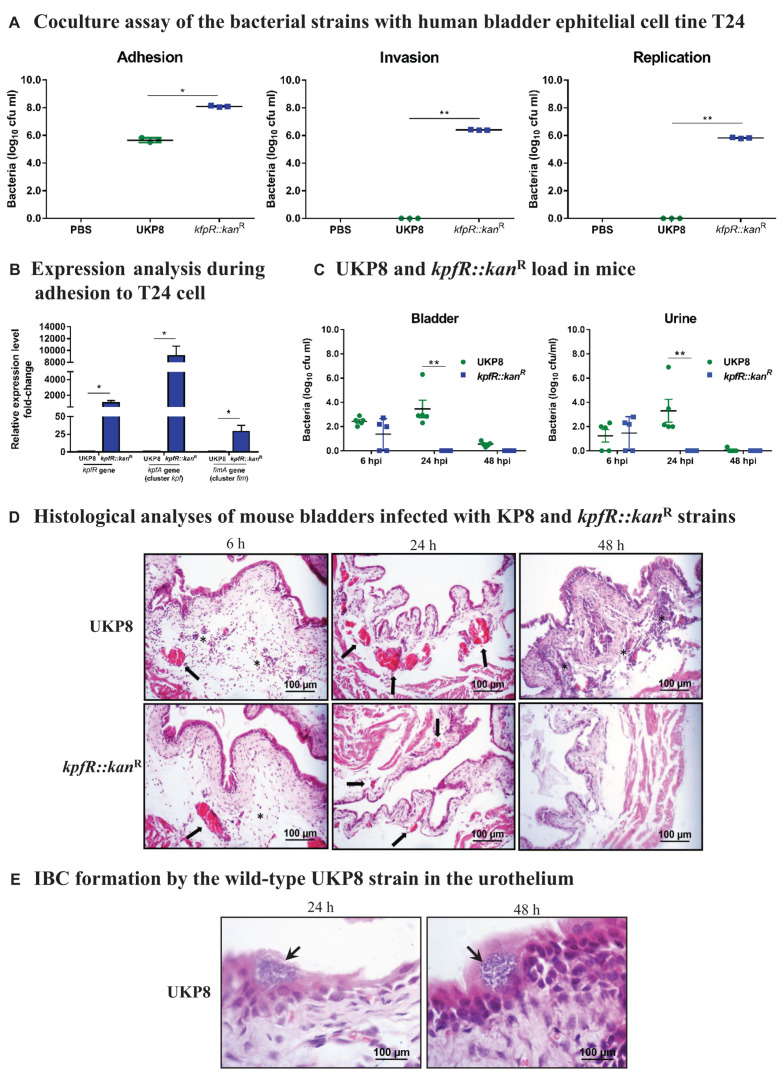
FIGURE 5.
K. pneumoniae mutant for kpfR adheres more efficiently and replicates within bladder epithelial cells, but loses resistance in the mouse model of urinary infection. For the coculture assays, human bladder epithelial cell line T24 were inoculated with the wild-type and kpfR::kanR strains at an MOI of 200 to assess the adhesion, invasion, and intracellular replication of the strains on the host human bladder cell. The incubation periods are described in section “Materials and Methods.” (A) The mutant strain has greater adhesion to T24 bladder cells than the wild-type UKP8 strain and is the only strain able to invade and replicate within T24 cells. (B) During adhesion to T24 bladder cells, the kpfR::kanR mutant strain have increased expression of kpfR and kpfA (cluster kpf) and fimA (cluster fim) than the wild-type UKP8 strain, which may explain the improved ability of the mutant strain to adhere the T24 cells. *p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01. For the mouse model of urinary infection, animals were inoculated by transurethral catheterization with 5 × 108 CFU/mL of UKP8 and kpfR::kanR strains. At the indicated times, the animals were euthanized, and urine and bladders were aseptically collected and processed for CFU enumeration and H&E staining. (C) Bacterial CFUs were counted on urine and bladder tissue after 6, 24, and 48 hpi with UKP8 and kpfR::kanR strains. In mice urine, the wild-type strain is recovered at 6 and 24 hpi, while the mutant kpfR::kanR strain is recovered only at 6 hpi. In the bladder tissue, the wild-type is present at 6, 24, and 48 hpi, whereas the mutant strain is also recovered only after 6 hpi. Mice are represented by symbols. Data were statistically analyzed by ANOVA test. **p ≤ 0.01. (D) Histological analyses of bladders infected with the wild-type and kpfR::kanR mutant strains show both strains triggering an inflammatory infiltrate consisting of neutrophils (asterisks) and a hyperemia (arrows) at 6 hpi. At 24 hpi, the hyperemia is more pronounced with the wild-type strain, and inflammatory cells migration is observed at 48 hpi only with UKP8, suggesting that at this period of infection the mutant strain has already been completely eliminated. Images are from an individual representative experiment. (E) Only the wild-type UKP8 is able to form biofilm-like intracellular bacterial communities (IBCs) in the urothelium of mice. Images from histological analyses of bladders infected with the wild-type at 24 and 48 hpi reveal IBCs (arrows) within superficial urothelial cells. Images are from an individual representative experiment.