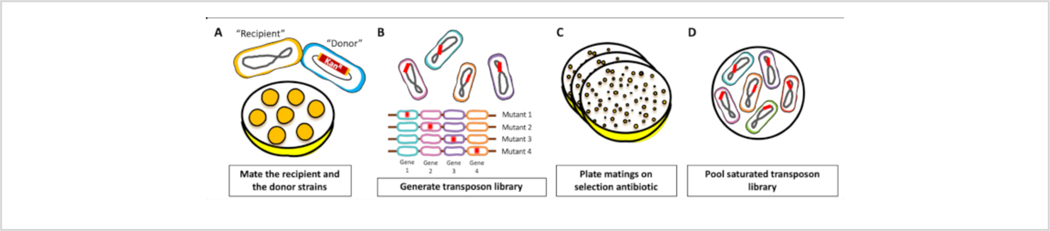
Figure 1: Schematic of transposon mutant library construction.
(A) Bacterial conjugation. The “donor” strain, which encodes the transposition machinery, was mixed with the “recipient” strain. The mixture was spotted on LB agar plates and allowed to mate for 1 h. (B) Generation of transposon library. The plasmid carrying the transposition machinery was transferred from the “donor” strain to the “recipient” strain and the transposon was randomly inserted throughout the genome of the “recipient” strain. (C) Selection. Resulting cells were plated on agar plates supplemented with kanamycin to select for transposon insertion mutants. (D) Pooled library. Colonies were scraped from plates, resuspended in LB and pooled. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.