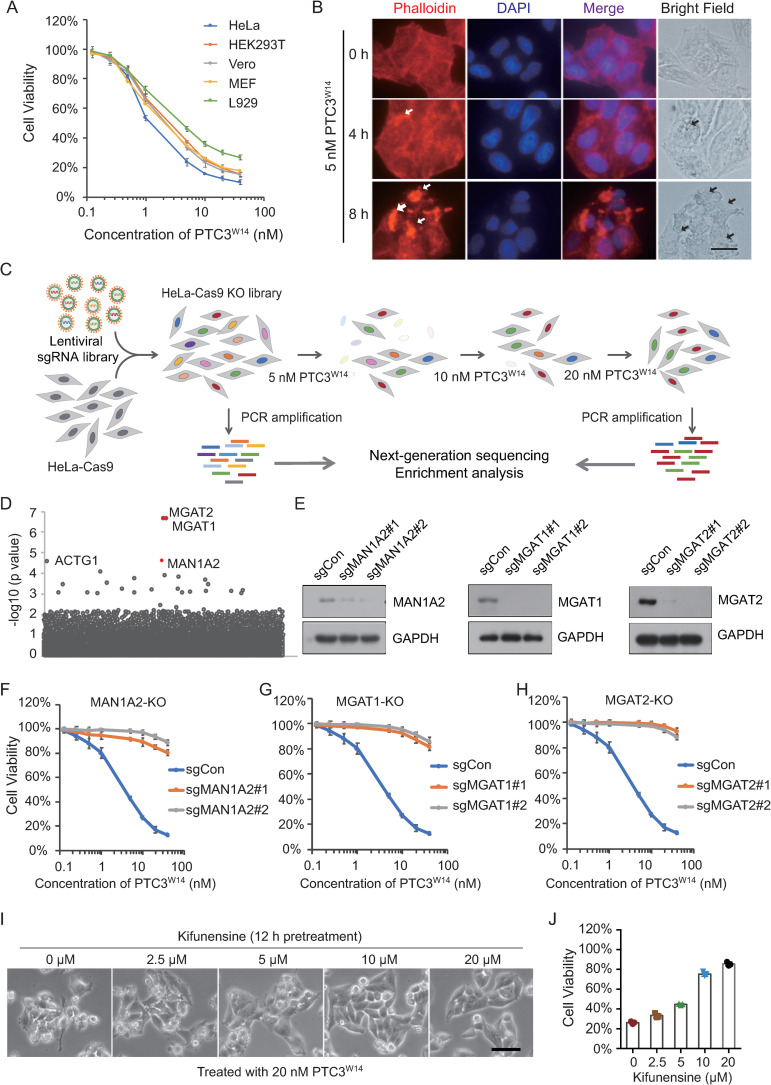
Fig 1. N-linked Glycans are required for the cell targeting of the TcdA1W14 pentamer.
(A) Five mammalian cell lines were treated with the indicated doses of PTC3W14 for 24 h. Cell viability was measured using CCK-8 assays. The PTC3W14 concentration that leads to the death of 50% of cells is defined as IC50. (B) HeLa-Cas9 cells transduced with a non-targeting sgRNA were treated with 5 nM PTC3W14 for 0, 4 and 8 h. Cells were fixed, permeabilized and stained with Alexa 568-phalloidin (red) and DAPI (blue). Representative fluorescence and bright field micrographs are shown. White arrows indicate polymerized F-actin. Black arrows indicate membrane blebs. Scale bars, 5 μm. (C) Schematic drawing of the screening approach for host factors that are critical for the intoxication of PTC3W14. HeLa cells stably expressing Cas9 (HeLa-Cas9) were transduced with lentiviral GeCKO v.2 sgRNA libraries. These cells were exposed to increased doses of PTC3W14 (5, 10 and 20 nM). Cells that were not treated with PTC3W14 were served as controls. Total genomic DNA from 2×107 selected and control cells was used for sequencing. The enriched sgRNAs were sequenced by NGS, followed by MAGeCK analysis. (D) Genes identified in the screens with PTC3W14 treatment were ranked based on to the MAGeCK p values. MAN1A2, MGAT1, and MGAT2 were identified as the key genes for PTC3W14 recognition of HeLa cells. (E) The efficiency of gene knockout was determined by Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. GAPDH served as the loading control. (F-H) MAN1A2-KO, MGAT1-KO, and MGAT2-KO HeLa-Cas9 cells were treated with the indicated doses of PTC3W14 for 24 h. Cell viability was measured using CCK-8 assays. (I-J) HeLa-Cas9-sgCon cells were pretreated with the indicated doses of Kifunensine for 12 h, and then exposed to 20 nM PTC3W14. Representative bright field micrographs were shown (I). Cell viability was measured using CCK-8 assays (J). All error bars indicate mean ± SD. Each of the experiments was repeated three times.