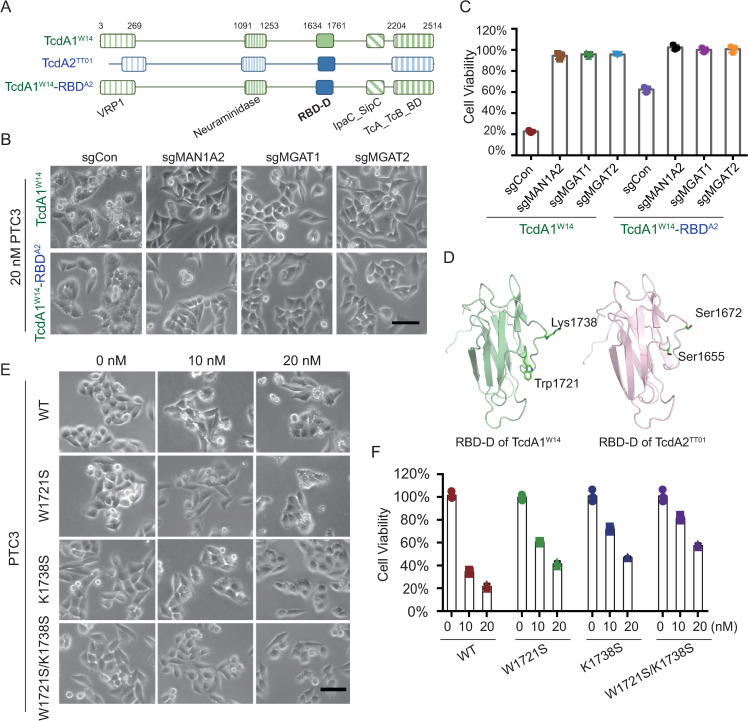
Fig 3. The Trp1721 and Lys1738 of TcdA1W14 are critical for N-glycan-mediated intoxication.
(A) Schematic drawing of TcdA1W14, TcdA2TT01 and TcdA1W14-RBDA2. The RBD-D domains derived from TcdA1W14 and TcdA2TT01 are depicted in green and blue, respectively. (B-C) MAN1A2-KO, MGAT1-KO, MGAT2-KO, and HeLa-Cas9-sgCon cells were exposed to 20 nM of the indicated Tc toxins. Representative bright field micrographs (B) and the effects on cell viability (C) are shown. (D) Homology models of RBD-D domains. Swiss model program (ExPASy web server) was used to construct a homology model of the RBD-D of TcdA2TT01 by alignment with that of TcdA1W14 (PDB: 4O9Y). The Trp1721 and Lys1738 residues of TcdA1W14 (corresponding to Ser1655 and Ser1672 of TcdA2TT01) are indicated. (E-F) Representative bright field micrographs of indicated HeLa-Cas9 cells treated with the indicated doses of wild-type PTC3W14 and indicated mutants (W1721S, K1738S, W1721S/K1738S) (E). Cell viability was measured using CCK-8 assays and shown in (F). All error bars indicate mean ± SD. Each of the experiments was repeated three times.