Figure 1:
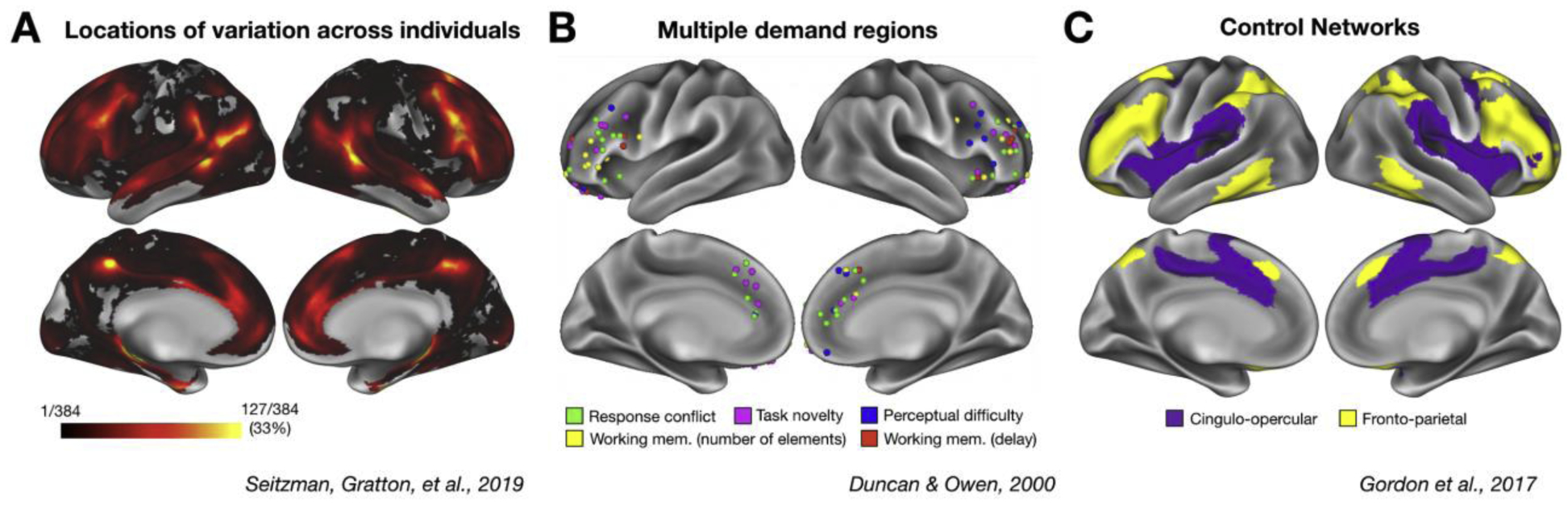
Locations of variation across individuals overlap with locations associated with cognitive control. (A) Locations of the cortex where individuals differ strongly from the typical group architecture (adapted from Seitzman and colleagues [14]; warmer colors represent more common sites of variation, with regions in yellow representing sites that vary in at least 33% of individuals. (B) Coordinates reported by Duncan and Owen [7] for sites with cognitive control related task activations. (C) The group-level cinguloopercular (purple) and frontoparietal (yellow) “control” networks originally identified by Gordon and colleagues from resting-state fMRI data [13]. Note the overlap between cognitive control regions/networks and locations of individual variability.
