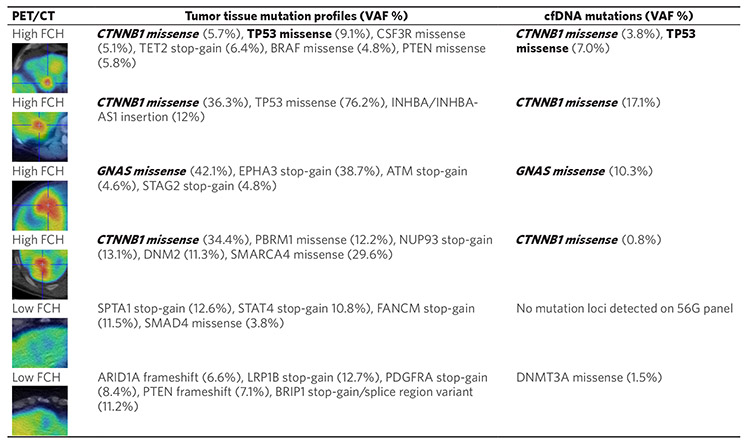
Figure 2.
Comparison of mutation profiling results obtained from pre-treatment cfDNA and post-resection tumor DNA in six HCC patients imaged by 18F-FCH PET/CT preoperatively. Mutations that show correspondence between tumor DNA and cfDNA are shown in bold. Mutations associated with aberrant Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation are italicized. On the liver PET/CT images shown in the first column, the tumors displaying high FCH uptake appear red on the rainbow color scale applied to these images. Note: A DNMT3A mutation found in the cfDNA but not the tumor DNA of one patient (bottom row) is likely due to clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP). CHIP-associated mutations arise from hematopoietic cells and are age-related. They are often encountered incidentally through cfDNA sequencing[55,56]. DNMT3A is the most frequently mutated gene associated with CHIP[57,58]. VAF: variant allele frequency