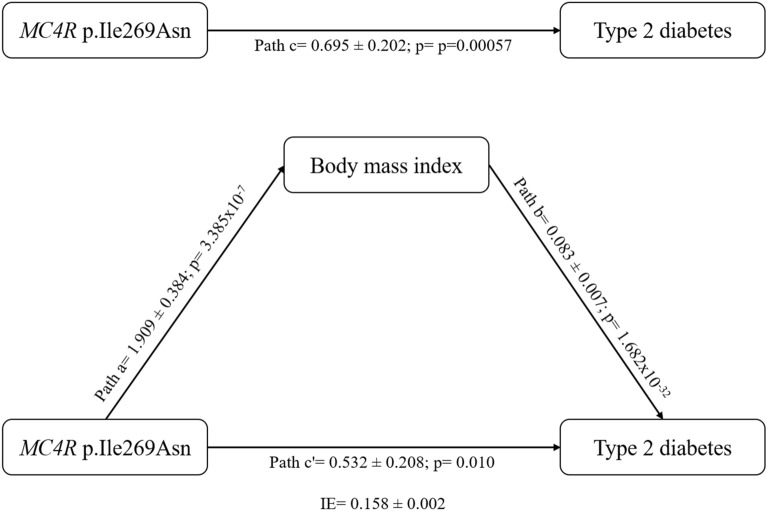
Figure 1.
Simple mediation model evaluating the effect of body mass index as a mediator of the association between MC4R p.Ile269Asn and type 2 diabetes (% of mediation = 22.7%, Sobel test: z = 4.584; p = 4.55 × 10–6). Path a, effect of MC4R p.Ile269Asn on body mass index (data is expressed as beta value ± standard error analyzed by a linear regression model adjusted for age and sex); Path b, effect of body mass index on type 2 diabetes (data is expressed as Log Odds Ratio ± standard error analyzed by a logistic regression model controlled for MC4R p.Ile269Asn, and adjusted for age and sex); Path c, total effect of MC4R p.Ile269Asn on type 2 diabetes (data is expressed as Log Odds Ratio ± standard error analyzed by a logistic regression model adjusted for age and sex); Path c′, effect of MC4R p.Ile269Asn on type 2 diabetes (data is expressed as Log Odds Ratio ± standard error analyzed by a logistic regression model controlled for body mass index, and adjusted for age and sex); IE, indirect effect of MC4R p.Ile269Asn on type 2 diabetes (data is expressed as the product of path a and path b); % of mediation is computed as IE divided by path c.